A PRIMARY KEY constraint in SQL Server is a field or column which ensures that each entry in a table is must be unique and not null.
A primary key can be created at the column or table level. The following is an example to illustrate this:
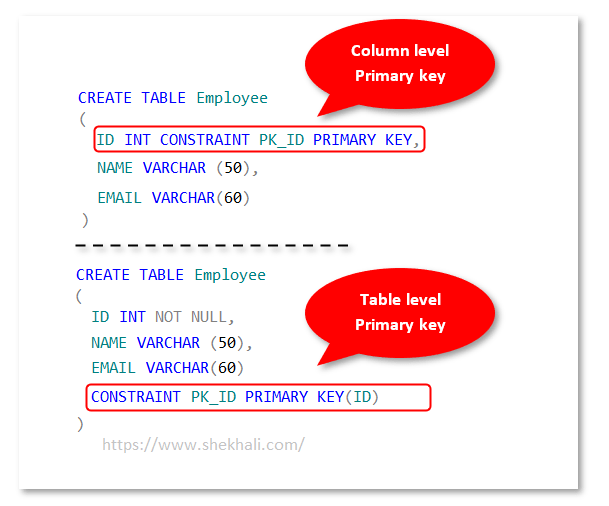
The primary key constraint ensures that the value(s) of the primary key column(s) is unique for every row in the table and cannot be null. In this article, we will explore the benefits and limitations of using primary keys in SQL Server and how to create and manage them effectively.
Table of Contents
- 1 What is the primary key in SQL Server?
- 1.1 Syntax to create a primary key
- 1.2 Creating Primary Key Using Create Table Statement
- 1.3 Can we add duplicate value in the primary key column?
- 1.4 Can we Insert NULL value in the primary key column?
- 1.5 How to Drop primary key constraint in SQL Server?
- 1.6 How to Create a composite primary key in the SQL server?
- 2 Advantages of the primary key in SQL Server
- 3 Limitations of the primary key constraint in SQL Server:
- 4 Conclusion
- 5 FAQs
- 5.1 Q:What is a Primary Key in SQL Server?
- 5.2 Q: Can a table have more than one Primary Key in SQL Server?
- 5.3 Q: Can a Primary Key column have NULL values in SQL Server?
- 5.4 Q: Can a Primary Key be changed in SQL Server?
- 5.5 Q: Is a Primary Key always clustered in SQL Server?
- 5.6 Q: What is the difference between a Primary Key and a Unique Key in SQL Server?
- 5.7 Related
What is the primary key in SQL Server?
A primary key in SQL is a column or set of columns that uniquely identify each row in a table. The primary key column must contain unique and non-null values. It ensures that there are no duplicate rows in the table and provides a fast way to search for specific records.
- When you create a primary key on a table column, the database engine automatically creates a unique index on that column.
- A primary key column doesn’t allow inserting
nullor duplicate values. - A Primary key can consist of up to 16 columns.
- A table can have only one primary key which can be applied to single or multiple columns.
- The primary key which consists of multiple columns is known as the
Composite primary key. - A Primary Key constraint can be applied to the columns having any data types.
- A primary key by default creates a
clustered indexon the column.
Syntax to create a primary key
The following is the syntax to create a primary key in the SQL server.
-- Column level Primary key
CREATE TABLE TableName
(
Column1 data_type [NOT NULL ] [ PRIMARY KEY ],
Column2 data_type [ NULL | NOT NULL ],
Column3 ...
);
-------------------------------
-- Creating table level Primary key
CREATE TABLE TableName
(
Column1 data_type [ NULL | NOT NULL ],
Column2 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ],
Column3 ...
CONSTRAINT ConstraintName PRIMARY KEY (Column1, Column2)
);
Creating Primary Key Using Create Table Statement
The following SQL query will create a Primary Key on the ID column when the Employee table is created.
-- Column level Primary key
CREATE TABLE Employee
(
ID INT CONSTRAINT PK_ID PRIMARY KEY,
NAME VARCHAR (50),
EMAIL VARCHAR(60)
)
-- OR
-- Table level Primary key
CREATE TABLE Employee
(
ID INT NOT NULL,
NAME VARCHAR (50),
EMAIL VARCHAR(60)
CONSTRAINT PK_ID PRIMARY KEY(ID)
)
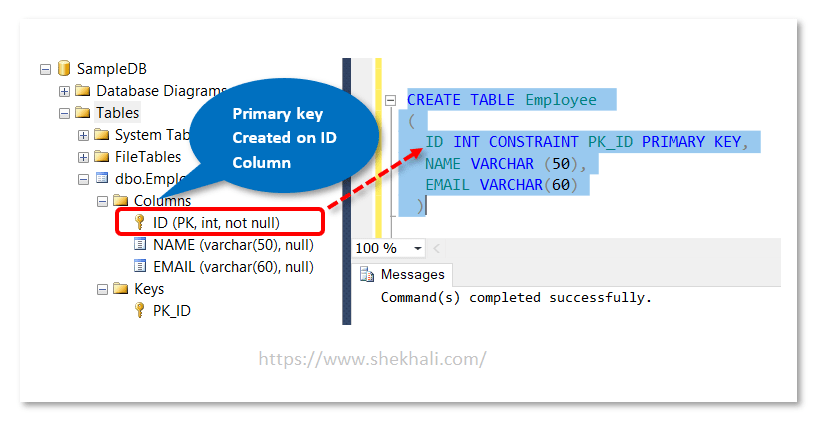
Let’s execute the above SQL query where we have created a primary key on the ID column of the employee table.
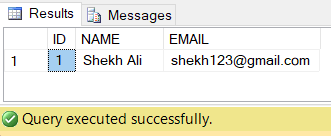
Let’s execute the following SQL insert statement to add a new record to the Employee table.
-- Insert a new record into the Employee table.
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES(1,'Shekh Ali','shekh123@gmail.com');
Can we add duplicate value in the primary key column?
Primary key columns do not accept duplicate values. Attempting to insert the same value that is already in the primary key column will result in an error.
Let’s execute the following SQL INSERT statement with duplicate values.
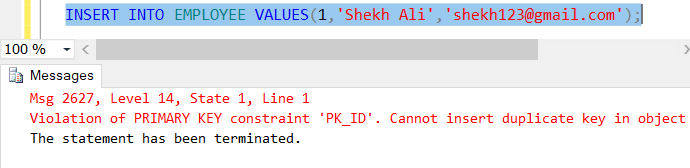
Here, we can see in the above example that the primary key doesn’t allow us to insert the duplicate records in the table.
Can we Insert NULL value in the primary key column?
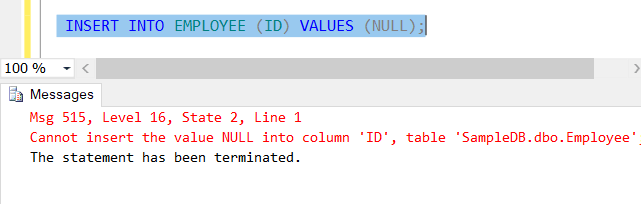
The primary key column doesn’t accept the NULL value. If we try to insert the null value in the primary key column, It will throw an error.
-- Insert NULL value into the primary key column.
INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE (ID) VALUES (NULL);
How to Drop primary key constraint in SQL Server?
Let’s drop a primary key constraint in the SQL server using the ALTER table statement.
-- Drop primary key constraint
ALTER TABLE Employee DROP CONSTRAINT PK_ID ;
How to Create a composite primary key in the SQL server?
The primary key consists of multiple columns or fields is known as the Composite primary key. In the following example, we will create a composite primary key on multiple columns such as ID and EMAIL.
First, let’s make the EMAIL column non-nullable. Otherwise, an error will occur when creating the composite primary key.
-- Make EMAIL column not nullable.
ALTER TABLE Employee ALTER COLUMN EMAIL VARCHAR(60) NOT NULL ;
Now let’s create a composite primary key.
-- Create composite primary key
ALTER TABLE Employee ADD CONSTRAINT EMP_PK PRIMARY KEY (ID, EMAIL);
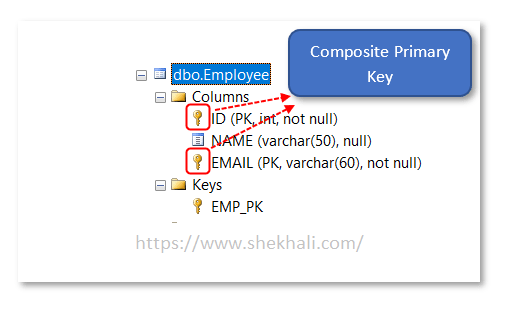
Here in the above image, we can see that the Composite primary key is applied over multiple columns (Ex: ID and EMAIL Columns).
Advantages of the primary key in SQL Server
- Uniqueness: Primary key ensures the uniqueness of each record in a table, which helps maintain data integrity.
- Indexing: SQL Server automatically creates a clustered index on the primary key column, which makes data retrieval faster.
- Joining tables: Primary key is used to join tables in a database. When a table is joined with another table, the primary key of one table is matched with the foreign key of the other table.
- Data validation: Primary key constraints can be used to validate data before it is entered into a table. This helps to ensure that the data entered into the table is valid and accurate.
- Data integrity: Primary key constraints help to maintain data integrity by preventing duplicate records from being inserted into a table.
- Simplifies database design: Primary keys provide a simple and straightforward way to identify records within a table. This makes it easier to design and maintain a database.
- Supports normalization: Primary keys are an essential part of database normalization. Normalization helps to reduce data redundancy and improve data consistency.
Limitations of the primary key constraint in SQL Server:
The limitations of the primary key constraint in SQL Server are as follows:
- Unique values only: The primary key constraint allows only unique and non-null values in the column(s). Therefore, it cannot have any duplicate values or NULL values.
- Limited number of columns: A primary key can be created on one or more columns, but there is a limit to the number of columns that can be included. In SQL Server, a primary key can have a maximum of 16 columns.
- Performance impact: As the primary key constraint enforces uniqueness, it can impact the performance of data insertion and updates. This is because the database has to check for duplicates each time data is inserted or updated.
- Additional index creation: When a primary key constraint is created on a table, SQL Server automatically creates a unique index on the column(s) defined as a primary key. This index can take up additional disk space and can affect the performance of data retrieval operations.
- Number of Indexes: The number of indexes on a table cannot exceed 999 nonclustered indexes and one clustered index, which includes the index created by the primary key constraint.
Reference: Primary Key Constraints
Conclusion
In conclusion, a primary key is a fundamental concept in SQL Server and is used to ensure the uniqueness and integrity of data in a table. By defining a primary key, you can prevent duplicate entries and enforce referential integrity between tables using foreign keys. A well-designed primary key can also improve the performance of database operations.
Choosing the appropriate data type is important and ensuring that the primary key values are unique and immutable. You can create a robust and efficient database system by following best practices for primary key design.
FAQs
Q:What is a Primary Key in SQL Server?
A Primary Key is a column or a set of columns in a table that uniquely identifies each row or record in that table. It enforces data integrity by ensuring that no two rows in the table can have the same primary key value.
Q: Can a table have more than one Primary Key in SQL Server?
No, a table can have only one Primary Key in SQL Server. However, a Primary Key can be made up of multiple columns, which is called a composite Primary Key.
Q: Can a Primary Key column have NULL values in SQL Server?
No, a Primary Key column cannot have NULL values in SQL Server. It must have a unique value for each row in the table, and NULL is not unique.
Q: Can a Primary Key be changed in SQL Server?
Yes, it is possible to change a Primary Key in SQL Server. However, it requires dropping and recreating the Primary Key constraint, which can be time-consuming and may affect the table’s performance.
Q: Is a Primary Key always clustered in SQL Server?
No, a Primary Key is not always clustered in SQL Server. However, by default, SQL Server creates a clustered index on the Primary Key column(s) to optimize data retrieval. If needed, it is possible to create a non-clustered index on a Primary Key instead of a clustered one.
Q: What is the difference between a Primary Key and a Unique Key in SQL Server?
A Primary Key and a Unique Key in SQL Server enforce uniqueness in a column or set of columns. However, a Primary Key also enforces the NOT NULL constraint, while a Unique Key allows NULL values. Additionally, a table can have only one Primary Key but multiple Unique Keys.
You might want to read this too:
- How to Create Foreign key in SQL?
- Mastering Database Normalization: Best Practices and Techniques
- Clustered Vs Non-Clustered Index in SQL
- Mastering SQL Inner Join
- Understanding CRM Databases
- Types of Joins in SQL Server
- Having VS Where Clause in SQL
- SQL EXISTS – Exploring EXISTS Operator in SQL Server
- Top 10 Differences between Stored Procedure and Function in SQL Server
- Like operator in SQL
- Different ways to delete duplicate rows in SQL Server
- SQL Comparison Operators (Less than, Greater than, Equal, Not Equal operators)
- View In SQL | Types Of Views In SQL Server
- Function vs Stored procedure in SQL Server
- C# 12 New Features in 2025: What’s New with .NET 8 - April 11, 2025
- Difference Between WCF and Web API with Examples: A Comprehensive Guide - March 27, 2025
- PUT vs PATCH vs POST in REST API: Key Differences Explained With Examples - March 23, 2025