SQL commands are a set of instructions used for interacting with relational database management systems (RDBMS).
SQL (Structured Query Language) is the standard language for managing and manipulating data in databases like SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, Sybase, and Postgres.
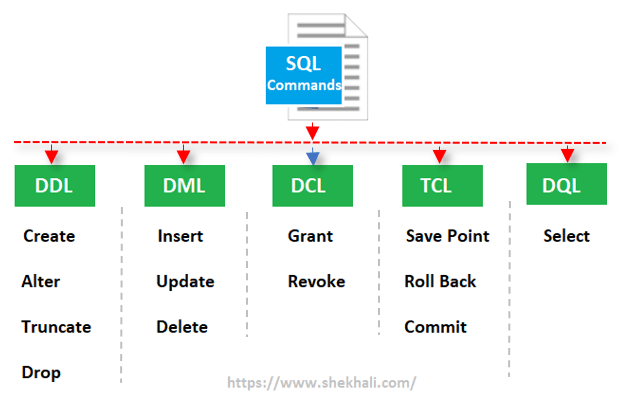
Here, We will learn SQL commands like DML, DDL, DCL, TCL and DQL commands in SQL with examples.
Database: A database is a place to store data in an electronic format. It is an organized collection of database objects such as tables, views, functions, stored procedures, triggers, and so on.
It allows a user to easily access or manipulate the data.
Table of Contents
Types of SQL Commands
The SQL commands are mainly categorized into five categories:
- DDL (Data Definition Language)
- DML (Data Manipulation Language)
- DCL (Data Control Language)
- TCL (Transaction Control Language)
- DQL (Data Query Language)
01. Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL, or Data Definition Language, is a subset of SQL (Structured Query Language) that is used for defining and managing the database schema.
In other words, DDL commands are used to create, modify, and delete database objects like tables, indexes, stored procedures, and constraints.
The following are some common DDL commands:
- CREATE
- ALTER
- SP_RENAME
- TRUNCATE
- DROP
CREATE
CREATE: The CREATE statement is used to create new database objects. For example, you can use it to create tables, views, functions, stored procedures, indexes, or databases themselves.
When creating a table, you define the column’s name, data types, and constraints for that table.
CREATE command in SQL Server is used to create a new database object. It can be used to create a new table, view, function, stored procedure, etc. in the database.
Syntax:
-- Syntax to create a database
Create database DabaseName;
-- Syntax to create a table
CREATE TABLE Table_Name (
Column_Name1 Data_Type (Size),
Column_Name2 Data_Type (Size),
Column_NameN Data_Type (Size)
);Example:
Creates a database named ‘TestDB’. Let us create a database and table, which we will use as a reference throughout this article:
CREATE DATABASE TestDB;The following Create statement will create a new Employee table in the database.
Use TestDB; -- Using TestDB database.
-- Creating a new table
CREATE TABLE Employee
(
Id INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Salary DECIMAL(18, 2)
);
ALTER
ALTER: The ALTER statement is used to modify the structure of existing database objects.
You can use the ALTER statement to add, modify, or delete columns or constraints in an existing table. It can be used to change the data type of a column.
Syntax:
Alter syntax to add a new column in an existing table:
ALTER TABLE Table_Name ADD New_Column_Name Data_Type (Size);Example:
The following Alter command is used to add a new column in the Employee table.
ALTER TABLE Employee ADD City VARCHAR(20)
To change the data type and size of an existing column.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE Table_Name ALTER COLUMN Column_Name New_Data_Type (New_Size)Example:
The following Alter statement is used to change the data type and size of an existing column named City.
ALTER TABLE Employee ALTER COLUMN City NVARCHAR (100);
To delete existing column from a table using Alter command.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE Table_Name DROP COLUMN Column_NameExample:
The following Alter statement is used to drop an existing column City from the table.
ALTER TABLE Employee DROP COLUMN City;
SP_RENAME
In SQL Server SP_RENAME is basically a system-defined stored procedure, which can be used to change the column and table name.
To rename the existing column name.
Syntax:
SP_RENAME 'Table_Name.Old_Column_Name','New_Column_Name' ;Example:
The following SP_RENAME statement is used to change the existing column name from the Employee table.
SP_RENAME 'Employee.Name','EmployeeName';
To change the existing table name.
Example:
The following SP_RENAME statement is used to change the old table name to the new name.
SP_RENAME 'Employee','EmployeeDetails' ;
Truncate
TRUNCATE: The TRUNCATE statement is used to quickly delete all records from a table but retain the table structure. It doesn’t support the ‘where’ clause, that’s why we can’t delete a specific record.
Syntax:
TRUNCATE TABLE Table_NameExample:
The following TRUNCATE statement is used to delete all the rows from a table.
TRUNCATE TABLE EmployeeDetails
DROP
DROP: The DROP statement is used to delete an existing database object, such as a table, index, or view. It permanently removes the object from the database.
If we use the drop command on a table, the table including all the records and constraints will be removed from the database.
Syntax:
DROP TABLE Table_NameExample:
The following DROP statement is used to delete the EmployeeDetails table from the database.
DROP TABLE EmployeeDetails ;
02. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
In SQL Server, Data Manipulation Language (DML) is used for interacting with and manipulating data stored within a SQL Server database.
DML commands allow you to perform operations such as retrieving, inserting, updating, and deleting data within database tables.
Here are some common DML commands in SQL Server:
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
INSERT
The INSERT statement is used to add new rows (records) to a table in the database.
Syntax:
INSERT INTO Table_Name (Column_Name1, Column_Name2, ColumnN)
VALUES (Value1, Value2, ValueN);Example:
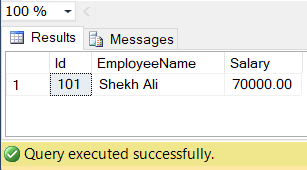
The following INSERT statement is used to add a new row in the EmployeeDetails table.
INSERT INTO EmployeeDetails( Id, EmployeeName, Salary)
VALUES (101, 'Shekh Ali', 70000);
UPDATE
The UPDATE statement in the SQL server is used to change or modify the existing records in a table.
Syntax:
-- Command to update the specific records based on where condition.
UPDATE Table_Name
SET Column_Name1 = Value1, Column_Name2 = Value2, ColumnN = ValueN
WHERE condition;
-- To update all the records for the particular columns
UPDATE Table_Name
SET Column_Name1 = Value1, Column_Name2 = Value2, ColumnN = ValueN;Example:
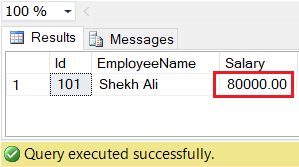
The following UPDATE statement is used to modify an existing record in the EmployeeDetails table.
-- Update Salary based on employee Id
UPDATE EmployeeDetails SET Salary = 80000
WHERE Id = 101;
When updating records in a table, you should be extremely careful.
because if you run the update query without the where clause, the table will be updated with all of the records for the selected columns.
DELETE
The DELETE command in SQL Server is used to delete one or more existing records from a table.
Syntax:
-- To delete specic records
DELETE FROM Table_Name WHERE condition;
-- OR
-- To delete all the records
DELETE FROM Table_Name ;Example:
The following DELETE statement is used to delete a specific record from the EmployeeDetails table.
DELETE FROM EmployeeDetails WHERE Id = 101 ;
To delete all the records from the EmployeeDetails table.
DELETE FROM EmployeeDetails ;
03. Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL, or Data Control Language, deals with the permissions, security, and access control aspects of a database management system.
DCL commands are used to control who can access specific database objects, what actions they can perform, and how data security is managed.
A user can grant various privileges on single or multiple tables. These permissions may be applicable for a user to use the commands such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, REFERENCES, ALTER, or ALL on a table.
There are two primary DCL commands in SQL:
- GRANT
- REVOKE
GRANT
GRANT: The GRANT command is used to give specific privileges or permissions to users or roles within a database.
These privileges can include the ability to perform actions like SELECT (read), INSERT (write), UPDATE (modify), DELETE (delete), and more on database objects such as tables, views, procedures, or even the entire database. For example, you can grant SELECT permission on a table to a user, allowing them to retrieve data from that table.
Syntax:
GRANT privileges ON object TO user;For example, If we want to grant a user named shekhali for the SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE privileges on a table called EmployeeDetails, we should run the following GRANT statement.
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON EmployeeDetails TO shekhali ;
- Grant user to create any table
GRANT CREATE ANY TABLE TO user
- Grant user to drop any table
GRANT DROP ANY TABLE TO user
REVOKE
REVOKE command is used to withdraw or take back some or all the user’s access privileges to the database objects given by using the GRANT command.
Syntax:
REVOKE privileges ON object FROM user;Example:
REVOKE SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON EmployeeDetails FROM shekhali ;
Following is the command to withdraw privileges from the user.
REVOKE CREATE, DROP TABLE FROM user
04. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
The TCL commands in SQL Server are used to manage the transaction and the changes made by DML statements like INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE in a table.
The following are the TCL Commands:
- COMMIT
- ROLLBACK
- SAVEPOINT
COMMIT
COMMIT: The COMMIT command is used to save all the changes made during a transaction and make them permanent in the database.
If there are no errors during the transaction, the changes are made permanent; otherwise, if there are any issues, the transaction can be rolled back to undo the changes.
After saving all the changes, Commit ends the current transaction and releases the transaction locks acquired on the tables.
Syntax:
COMMIT;Example:
Let’s insert some records in the table.
BEGIN TRANSACTION
INSERT INTO EmployeeDetails(Id,EmployeeName,Salary) VALUES(102,'ALI',50000);
INSERT INTO EmployeeDetails(Id,EmployeeName,Salary) VALUES(103,'Klara',60000);
if(@@ERROR > 0)
BEGIN
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION;
END
BEGIN
COMMIT TRANSACTION;
END
Let’s run the above transactions to insert the records.
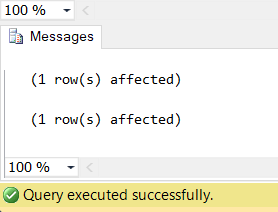
Let’s see the result by using the SELECT statement.
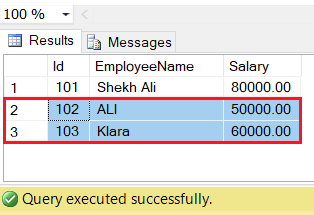
ROLLBACK
ROLLBACK: The ROLLBACK command is used to undo all the changes made during a transaction and restore the database to its state before the transaction begins.
It is typically used when an error or unexpected issue occurs during a transaction, and you want to revert the database to its previous state to maintain data consistency.
After the rollback is done, it releases the transaction locks acquired on the tables.
Syntax:
ROLLBACK ;Example:
The following transaction will Rollback due to a violation of the primary key.
Let’s insert some records with the same Id key that already exists in the table.
BEGIN TRANSACTION
INSERT INTO EmployeeDetails(Id,EmployeeName,Salary) VALUES(104,'Sam',30000);
INSERT INTO EmployeeDetails(Id,EmployeeName,Salary) VALUES(103,'David',40000);
if(@@ERROR > 0)
BEGIN
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION;
END
BEGIN
COMMIT TRANSACTION;
END
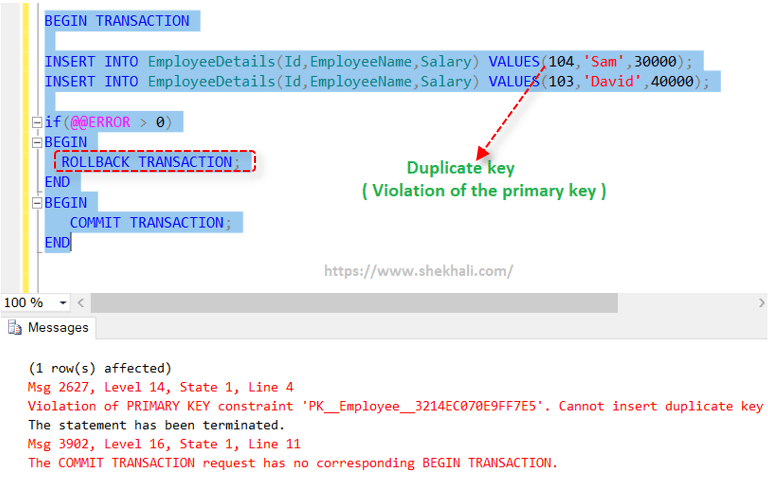
Save Transaction Command In SQL Server
The Savepoint command in SQL Server is used to save a transaction temporarily. So, that we can Rollback to a certain state or point whenever required.
Following is the syntax of the savepoint command.
SAVE TRANSACTION Savepoint_Name ;Example:
BEGIN TRANSACTION
INSERT INTO EmployeeDetails VALUES(104,'Sameer',30000);
-- Create a savepoint after the first INSERT
SAVE TRANSACTION A;
Update EmployeeDetails SET EmployeeName ='Priya' WHERE ID=104;
-- Create a savepoint after the Update
SAVE TRANSACTION B;
INSERT INTO EmployeeDetails VALUES(105,'David',40000);
-- Create a savepoint after the Insert
SAVE TRANSACTION C;
INSERT INTO EmployeeDetails VALUES(106,'John',70000);
-- Create a savepoint after the Insert
SAVE TRANSACTION D;
-- Rollback to the savepoint A
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION A;
COMMIT;
Let’s run the above transaction and see the result by using the SELECT Statement.
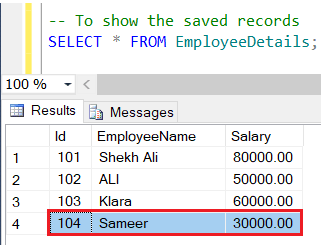
In the above result, we can see that the only record for the first insert statement is only committed because the transaction was Rollback to savepoint ‘A’ before the rest of the statements.
05. Data Query Language (DQL)
DQL (Data query language) is used to fetch the data from the database using a SELECT statement.
- The SELECT command is used to extract data from a database.
- It is used to select the attribute depending on the condition described by the WHERE clause.
Syntax:
SELECT expressions FROM Table_Name
WHERE conditions;Example:
-- To show all the records
SELECT * FROM EmployeeDetails;
-- To show the records based on where condition
SELECT * FROM EmployeeDetails WHERE ID=101;
Example 2:
SELECT name
FROM student
WHERE age > 15;
Conclusion:
- SQL Server provides various DDL (Data Definition Language) commands to create and manipulate the database objects such as CREATE, ALTER, TRUNCATE, and DROP
- Using these commands a user can change the structure of the database objects.
- The DML (Data Manipulation Language) commands in SQL Servers are used to manipulate or modify the data stored in the database.
- These commands can be used to INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE the records from the database.
- The DCL (Data Control Language) commands in SQL Server mainly deal with the right, permissions, and other security-related jobs. These commands are GRANT and REVOKE.
I hope you enjoyed it and found it helpful. Please leave a comment and share this post with others.
References: SQL Commands
Recommended Articles:
- Types of Joins in SQL Server
- Function vs Stored procedure in SQL Server
- Stored Procedure in SQL Server With Examples
- Create, Alter, and Drop Database In SQL Server
- SQL Comparison Operators (Less than, Greater than, Equal, Not Equal operators)
- Primary Key Constraint In SQL Server
- View In SQL | Types Of Views In SQL Server
- SQL Server Trigger Update, Insert, Delete Examples
- Difference Between Array And ArrayList In C#: Choosing the Right Collection - May 28, 2024
- C# Program to Capitalize the First Character of Each Word in a String - February 21, 2024
- C# Program to Find the Longest Word in a String - February 19, 2024