The goto in C# is a jump statement that transfers the control to another part of the program.
In this article, we will learn in detail about the goto statement its advantages and disadvantages with code examples.
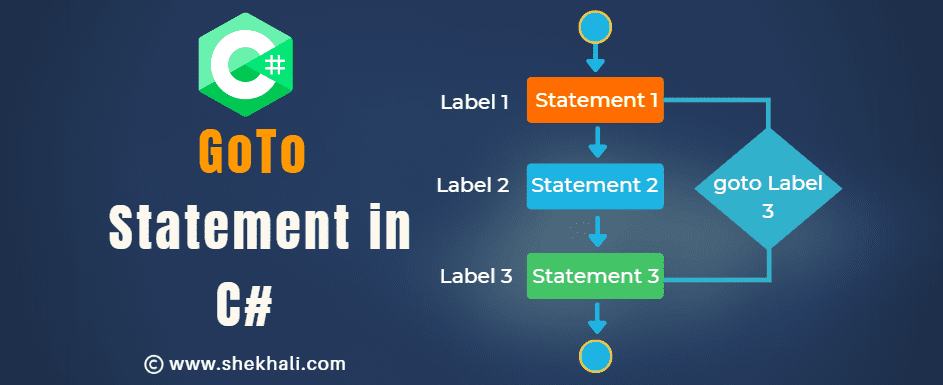
Table of Contents
- 1 C# Goto Definition:
- 2 Example 1: Breaking out of nested loops using goto in C#:
- 3 Example 2: Jumping to error handling code:
- 4 Example 3: Creating infinite loops using goto in C#:
- 5 Example 4: Using switch statement with goto in C#:
- 6 Pros and Cons of the C# Goto Statement:
- 7 FAQs
- 7.1 Q: What is the goto in C#?
- 7.2 Q: How does the goto statement work in C#?
- 7.3 Q: What are the advantages of using the goto statement in C#?
- 7.4 Q: What are the disadvantages of using the goto in C#?
- 7.5 Q: Can the goto statement be combined with other control statements in C#?
- 7.6 Q: What is an example of using the goto statement in C#?
- 7.7 Related
C# Goto Definition:
In C#, the goto statement is a jump statement used to transfer control to a labelled statement within the same method, switch statement, or loop.
However, the use of goto is generally discouraged in modern programming practices because it can make code harder to understand and maintain.
Here is a simple example of how goto can be used in C#:
using System;
class GotoExample
{
static void Main()
{
int counter = 0;
// The label where the program can jump to
start:
Console.WriteLine($"Counter: {counter}");
counter++;
// Check if counter is less than 5
if (counter < 5)
{
// Jump to the 'start' label
goto start;
}
Console.WriteLine("End of program");
}
}
Output:
Counter: 0
Counter: 1
Counter: 2
Counter: 3
Counter: 4
End of programCode Explanation:
In this example, the program uses a goto statement to jump back to the labelled statement “start” as long as the counter is less than 5.
However, it’s important to note that in most cases, using structured control flow statements like for, while, and do-while is preferred over goto, as they lead to more readable and maintainable code.
We can use the goto statement in many different scenarios in C# programming such as:
- Breaking out of nested loops
- Jumping to error handling code
- Creating infinite loops
- Controlling the flow of complex logic
Example 1: Breaking out of nested loops using goto in C#:
In C#, We can use the goto statement to break out of nested loops. It can be especially useful when multiple nested loops are used, and the programmer wants to exit them simultaneously.
using System;
using System.IO;
namespace GotoExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// loop through values of i from 0 to 4
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
// nested loop through values of j from 0 to 4
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
// output the values of i and j
Console.WriteLine("i: {0}, j: {1}", i, j);
// if j is equal to 2, jump to the label "end"
if (j == 2)
{
goto end;
}
}
}
end:
Console.WriteLine("Outside loops");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:
i: 0, j: 0
i: 0, j: 1
i: 0, j: 2
Outside loops
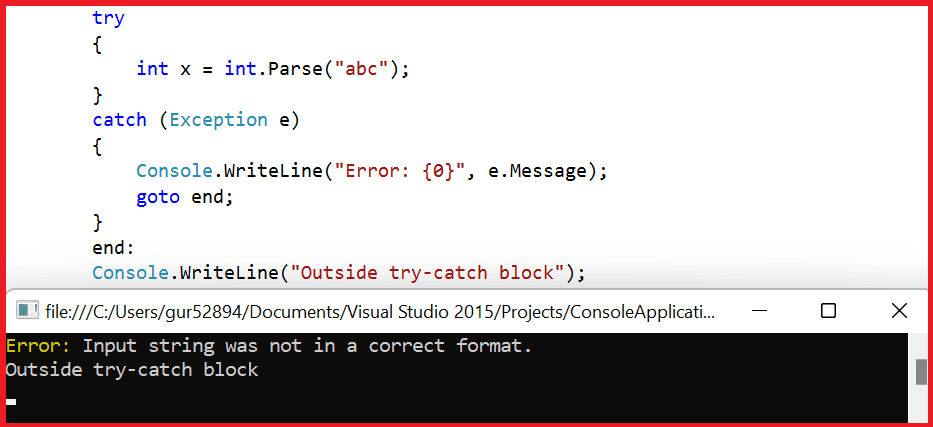
Example 2: Jumping to error handling code:
In C#, the goto statement can redirect the program flow to the error handling code in case an error occurs.
It could be helpful in scenarios where the error handling code is not located near the source of the error, and the programmer intends to make it easily accessible.
using System;
using System.IO;
namespace SystemIOExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
int x = int.Parse("abc");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: {0}", e.Message);
goto end;
}
end:
Console.WriteLine("Outside try-catch block");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
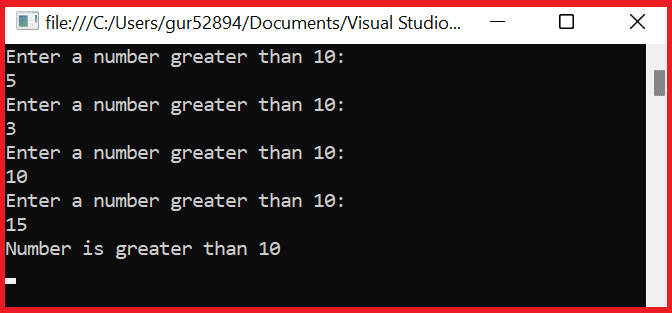
Example 3: Creating infinite loops using goto in C#:
The goto in C# can be used to create infinite loops. It can be beneficial when the programmer wants to run a loop continuously until a specific condition is met.
// Start label to repeat the process if the number entered is not greater than 10
start:
// Prompt user to enter a number greater than 10
Console.WriteLine("Enter a number greater than 10:");
// Read the user input and store it in the "number" variable
int number = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
// Check if the number entered is less than or equal to 10
if (number <= 10)
{
// If the number is not greater than 10, go back to the start label
goto start;
}
else
{
// If the number is greater than 10, print a message
Console.WriteLine("Number is greater than 10");
}
Console.ReadLine();
Output:
Example 4: Using switch statement with goto in C#:
We can also combine the goto statement with the switch statement in C#. This example demonstrates how we can implement a label within the switch statement to jump to a specific case.
Let’s take an example of a program that calculates the day of the week based on the number entered by the user.
using System;
namespace GotoExample4
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter a number between 1 to 7:");
int day = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
switch (day)
{
case 1:
Console.WriteLine("Monday");
break;
case 2:
Console.WriteLine("Tuesday");
break;
case 3:
Console.WriteLine("Wednesday");
break;
case 4:
Console.WriteLine("Thursday");
break;
case 5:
Console.WriteLine("Friday");
break;
case 6:
Console.WriteLine("Saturday");
break;
case 7:
Console.WriteLine("Sunday");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("Invalid Input");
goto end;
}
Console.WriteLine("Thank you for using the program.");
end:
Console.WriteLine("Exiting the program.");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Output:
Enter a number between 1 to 7:
5
Friday
Thank you for using the program.
Exiting the program.
Pros and Cons of the C# Goto Statement:
Certainly! While the goto statement in C# can be used in certain situations, it comes with both advantages and disadvantages. Here are the pros and cons of using the goto statement in C#:
Pros:
- Simplifying Control Flow:
gotocan be useful in certain scenarios where it simplifies control flow, especially when dealing with nested loops or complex switch statements.
- Code Reusability:
- In some cases,
gotocan be used to create reusable code blocks, as it allows you to jump to a specific labeled statement.
- In some cases,
- Legacy Code Compatibility:
- When working with legacy code or maintaining code written by others, you may encounter the use of
goto. Understanding its usage can be necessary for handling such scenarios.
- When working with legacy code or maintaining code written by others, you may encounter the use of
Cons:
- Readability and Maintainability:
- The primary disadvantage of using
gotois that it can make code less readable and harder to maintain. It disrupts the natural flow of code execution, making it difficult for developers to follow the logic.
- The primary disadvantage of using
- Spaghetti Code:
- Excessive use of
gotocan lead to “spaghetti code,” where the program’s structure becomes tangled and convoluted. This makes it challenging to understand, debug, and modify the code.
- Excessive use of
- Error-Prone:
- Misuse of
gotocan introduce subtle bugs and errors, especially when jumping across different parts of the code. It can lead to unexpected behavior and make it challenging to identify the source of issues.
- Misuse of
- Structured Alternatives:
- Modern programming languages, including C#, provide structured control flow statements like
if,for,while, andswitch. These alternatives are generally preferred for their clarity and maintainability.
- Modern programming languages, including C#, provide structured control flow statements like
- Not Recommended by Best Practices:
- The use of
gotois discouraged by coding standards and best practices in many programming communities. Most modern programming languages provide features that make structured control flow more expressive and readable.
- The use of
FAQs
Q: What is the goto in C#?
The goto statement in C# is a control statement that allows a programmer to transfer the flow of execution to another statement in the same function.
Q: How does the goto statement work in C#?
The goto statement transfers the flow of execution to a labeled statement in the same function. The programmer defines the label, and it is used as a destination for the goto statement.
Q: What are the advantages of using the goto statement in C#?
The advantages of using the goto statement in C# include its simplicity, ability to simplify complex logic, and ability to save time by reducing the need for multiple conditional statements.
Q: What are the disadvantages of using the goto in C#?
The disadvantages of using the goto statement in C# include its potential to make the code more difficult to maintain and debug. It will lead to unexpected results if used correctly and make the code less readable and easier to understand.
Q: Can the goto statement be combined with other control statements in C#?
Yes, we can use the goto statement in combination with other control statements, such as the switch statement in C#.
Q: What is an example of using the goto statement in C#?
An example of using the goto in C# is to jump to the error handling code when an error occurs in the program, making the error handling code easily accessible. Another example is implementing a label within a switch statement to jump to a specific case.
References: MSDN-Jump-Statements
Articles you might also like:
- C# Tutorial
- C# Programs asked in Interviews
- C# For Loop with examples
- C# While Loop with examples
- C# Do While Loop with examples
- if else vs switch condition
- Properties In C# with examples
- Local vs Global Variables
- C# stack vs heap
- IEnumerable Interface in C# with examples
- Constructors in C# with Examples
- C# Dictionary
- Is vs As operator in C#
- Abstract Factory Design Pattern in C#
- Singleton Design Pattern in C#
- Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit in C#
Please share this post and let us know what you think in the comments.
- C# 12 New Features in 2025: What’s New with .NET 8 - April 11, 2025
- Difference Between WCF and Web API with Examples: A Comprehensive Guide - March 27, 2025
- PUT vs PATCH vs POST in REST API: Key Differences Explained With Examples - March 23, 2025