
Table of Contents
- 1 Array VS List in C#
- 2 What is an Array?
- 3 C# List
- 4 Differences between arrays and lists in C#
- 5 Summary:
- 6 FAQs:
- 6.1 Q: What is the difference between an array and a list in C#?
- 6.2 Q: How do I declare and initialize an array in C#?
- 6.3 Q: How do I declare and initialize a list in C#?
- 6.4 Q: Can you change the size of an array after it is created?
- 6.5 Q: Can I change the size of a list after it is created?
- 6.6 Q: When should I use an array?
- 6.7 Q: When should I use a list?
- 6.8 Q: Which one is faster, an array or a list?
- 6.9 Q: Can I convert an array to a list and vice versa?
- 6.10 Q: Are there any other collection types in C#?
- 6.11 Related
Array VS List in C#
Here are the main differences between arrays and lists in C#:
- Fixed Size vs. Dynamic Size: Arrays have a fixed size that is defined when they are created, meaning you cannot easily change the size of an array once it has been initialized. Lists, however, can dynamically grow or shrink in size when elements are added or deleted.
- Type Safety: Arrays in C# can hold elements of a single data type only, whereas lists can hold elements of different data types because they are a part of the generic collection classes.
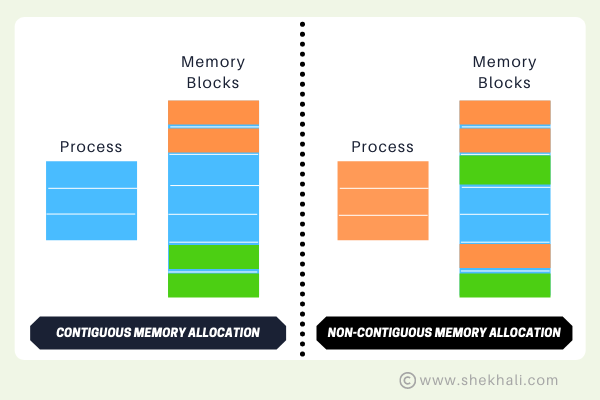
- Memory Allocation: Arrays are allocated in a contiguous block of memory, which can be more memory-efficient than lists, which may have to allocate additional memory when resizing. Lists use an underlying array that can be resized as needed.
- Methods and Properties: Arrays have a fixed set of properties and methods available, such as Length for the number of elements in the array. Lists, being a part of the generic collection classes, have additional methods and properties that make it easier to work with collections of data.
- Type Safety: Arrays in C# can hold elements of a single data type only, whereas lists can hold elements of different data types because they are a part of the generic collection classes.
- Performance: In general, arrays can be faster for direct access to elements by index because they are stored in contiguous memory locations whereas adding or deleting elements from a List is faster. Usually, Lists may perform slightly slower due to their dynamic resizing capabilities.
- Namespace: The C# List class is a part of the
System.Collections.Genericnamespace, whereas the Array class belongs to theSystem.Arraynamespace.
Code Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Program {
public static void Main(string[] args) {
// Initialize an array with a fixed size of 2 elements
int[] array = new int[2];
// Initialize a list with no elements
List<int> list = new List<int>();
// Display the initial length/count
Console.WriteLine("Initial length of array: " + array.Length);
Console.WriteLine("Initial count of list: " + list.Count);
// Reassign the array with a new size of 5 elements
array = new int[5];
// Add elements to the list
list.Add(1);
list.Add(2);
list.Add(3);
list.Add(4);
// Display the updated length/count
Console.WriteLine("Updated length of array: " + array.Length);
Console.WriteLine("Updated count of list: " + list.Count);
}
}Output:
Initial length of array: 2
Initial count of list: 0
Updated length of array: 5
Updated count of list: 4What is an Array?
Arrays: An array in C# is a fixed-size data structure that holds data of the same type. Once created, an array’s size cannot be changed.
Arrays are useful to use when you know the exact size of your collection in advance.
The Array class is available in the System.Array namespace.
You can access elements in an array using numeric indexes, starting from 0 (zero). The first item in the array is at index 0, the second is at index 1, and so on.
You can define an array by using square brackets “[]” and specifying the type of data it will hold (e.g., integers or strings) along with a name.
Creating an Array:
Let’s create an array of integers called intArray:
// Create an integer array called 'intArray' with a length of 5
int[] intArray = new int[5];
// Alternatively, you can initialize the array with specific values like this:
int[] intArray = new int[] {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// Now, 'intArray' contains the following values at different indexes:
// Index 0: 10
// Index 1: 20
// Index 2: 30
// Index 3: 40
// Index 4: 50
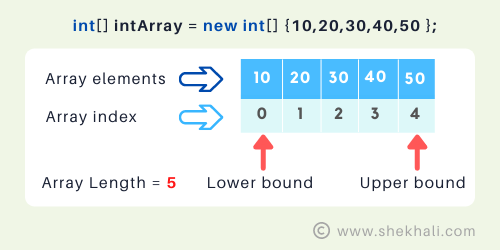
In this example, we created an array of integers called intArray with a capacity of 5 items. IntArray can hold five integers, and we can access each element using the indexes 0 to 4.
Accessing the elements of an Array:
You can create a string array with the following syntax:
using System;
namespace CSharpArrayExample
{
public class CSharpArrayExample
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Declare an array
string[] fruitsName = { "Apple", "Orange", "Banana", "Grapes"};
// Access the elements of an Array using index
Console.WriteLine(fruitsName[0]); // Output: Apple
// Access the elements using for loop
for(int index = 0; index < fruitsName.Length; index ++)
{
Console.WriteLine(fruitsName[index]);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
//Output:
// Apple
// Orange
// Banana
// Grapes
}
}Array memory allocation:
C# List
List: In C#, the List is a generic collection of strongly typed objects that can change its size dynamically when elements are added or removed. It is available in the System.Collection.Generic namespace.
Lists are appropriate when you need flexibility in the size of your collection.
You can access the List elements using index or loops. It enables you to perform different operations, such as sorting, searching, adding, and removing elements from the collection.
If you want to know more about the List class and how to use it in C#, you can check out my previous article, “C# List Class“.
Syntax:
The following is the syntax for declaring a generic List<T>. The parameter T in the List represents the type of item in the list, which can be int, long, string, or any user-defined object.
List<T> myList = new List<T>();C# List<T> example:
The following is an example of a List in C#.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace CSharpListExample
{
public class CSharpArrayExample
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Declare a generic List of string type
List<string> fruitsName = new List<string>();
// Add items in the List
fruitsName.Add("Apple");
fruitsName.Add("Orange");
fruitsName.Add("Banana");
fruitsName.Add("Grapes");
// Access the elements of a List using index
Console.WriteLine(fruitsName[0]); // Output: Apple
// Access the list elements using for loop
for(int index = 0; index < fruitsName.Count; index ++)
{
Console.WriteLine(fruitsName[index]);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
//Output:
// Apple
// Orange
// Banana
// Grapes
}
}Differences between arrays and lists in C#
Definition:
- An array is a fixed-size collection that stores elements of the same data type in contiguous memory locations.
- A list is a dynamic-size collection that can store elements of the same data type and automatically resizes itself as elements are added or removed.
Flexibility:
- An array is less flexible, as its size cannot be changed after creation. You need to create a new array with a different size if you want to change it.
- The list is more flexible, as you can add or remove elements without worrying about the size.
Performance:
- Arrays generally perform better for fixed-size collections due to contiguous memory and direct indexing.
- Lists might have a slight performance overhead due to dynamic resizing, but for most use cases, the difference is negligible.
Initialization:
- Elements in an array can be directly initialized during declaration.
- Elements in a list need to be added one by one, or you can initialize it with an existing collection.
Namespace:
- Arrays are part of the C# language and don’t require any additional namespace.
- Lists are part of the
System.Collections.Genericnamespace, so you need to import it.
Index Access:
- You can access elements in an array using index notation (e.g.,
array[index]). - Like arrays, you can access elements in a list using index notation (e.g.,
list[index]).
Element Types:
- Arrays can only hold elements of the same type (homogeneous).
- Lists can also hold elements of the same type (homogeneous) but can also hold different types using generics.
When to Use:
- Use Arrays when you know the exact size of the collection in advance and don’t need to change it frequently.
- Use Lists when you want a flexible collection that can grow or shrink as needed or when you need additional methods for data manipulation.
C# list vs array performance
Arrays allocate a fixed-size block of memory when initialized, making them suitable for scenarios where the size of the collection is known in advance. Lists, on the other hand, dynamically allocate memory, allowing them to grow or shrink as needed. Let’s explore this through code:
Array Example:
int[] integerArray = new int[5]; // Allocates memory for 5 integers
List Example:
List<int> integerList = new List<int>(); // Dynamically allocates memory
- Performance in Adding Elements:
Adding elements to a collection is a common operation, and the performance can vary between arrays and lists.
Array Example:
int[] integerArray = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
integerArray[i] = i;
}
List Example:
List<int> integerList = new List<int>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
integerList.Add(i);
}
Comparison:
Adding elements to a list is generally faster than resizing an array. Lists automatically handle resizing, resulting in better performance for dynamic collections.
- Accessing Elements:
Accessing elements by index is a fundamental operation. Let’s compare the syntax and performance for arrays and lists.
Array Example:
int value = integerArray[2]; // Accessing element at index 2
List Example:
int value = integerList[2]; // Accessing element at index 2
Comparison: Array access is marginally faster since arrays have a contiguous block of memory, allowing for direct indexing. Lists, being dynamic, may involve additional checks.
- Memory Overhead:
Lists have some memory overhead due to their dynamic nature and additional features. This can impact performance in scenarios where memory efficiency is important.
Array Memory Overhead: Arrays have minimal memory overhead, as they only store the elements and the necessary metadata.
List Memory Overhead: Lists carry additional metadata, such as capacity and count, leading to slightly higher memory overhead compared to arrays.
Summary:
The decision of whether to use arrays or lists in C# largely depends on the needs of your application. If you require a collection of a fixed size with faster access times, then arrays are the way to go. In contrast, if you need to frequently resize the collection or perform efficient insertion and deletion operations, then lists offer a more flexible solution.
I hope you enjoyed reading this article “C# array vs list“. If you find something incorrect or wish to offer more information regarding the topic addressed here, please leave a comment below.
FAQs:
Q: What is the difference between an array and a list in C#?
Q: How do I declare and initialize an array in C#?
For example, to declare an array of integers named “myArray,” you can use the syntax:
int[] myArray; To initialize the array with specific values, you can use the following syntax: int[] myArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};Q: How do I declare and initialize a list in C#?
System.Collections.Generic namespace. First, you declare a list by specifying the type of elements it will contain, followed by the name. For example, to declare a list of strings named “myList,” you can use the syntax:
List myList; To initialize the List, you can use the following syntax:
List myList = new List {"Apple," "Banana," "Mango"};Q: Can you change the size of an array after it is created?
Q: Can I change the size of a list after it is created?
Q: When should I use an array?
Q: When should I use a list?
Q: Which one is faster, an array or a list?
Q: Can I convert an array to a list and vice versa?
System.Linq namespace. For example,
List myList = myArray.ToList(); To convert a list to an array, you can use the ToArray() method. For example,
int[] myArray = myList.ToArray();Q: Are there any other collection types in C#?
Articles to Check Out:
- C# Tutorial
- C# Dictionary
- C# Hashtable
- Collections in C#
- C# Hashtable vs Dictionary vs HashSet
- C# Program asked in Interviews
- C# 12 New Features in 2025: What’s New with .NET 8 - April 11, 2025
- Difference Between WCF and Web API with Examples: A Comprehensive Guide - March 27, 2025
- PUT vs PATCH vs POST in REST API: Key Differences Explained With Examples - March 23, 2025