
Table of Contents
- 1 Collections in C#
- 2 C# Collections Workflow
- 3 01. Queue in C#
- 4 02. Stack in C#
- 5 03. Arrays in C#
- 6 04. Dictionary in C#
- 7 05. HashTable in C#
- 8 06. ArrayList in C#
- 9 07. C# SortedList
- 10 FAQs
- 10.1 Q: What are collections in C#?
- 10.2 Q: What is the difference between collection and array?
- 10.3 Q: Is ArrayList a generic collection in C#?
- 10.4 Q: What is the difference between Array and Arraylist Collections in C#?
- 10.5 Q: How many types of collections are there in C#?
- 10.6 Q: Why do we use collections in C#?
- 10.7 Q: How do I choose the right collection for my program?
- 10.8 Q: How are queues and stacks useful in C# collections?
- 10.9 Related
Collections in C#
A collection in C# is a class that represents a group of objects. Collections can be used to perform various operations on objects, such as storing, updating, deleting, retrieving, searching, and sorting.
Collections are defined in the System.Collections namespace. They are a predefined set of classes for storing multiple items in a single unit.
There are different types of collections in C#, such as Arrays, Stack, Queue, HashTable, ArrayList, Dictionary, and SortedList, etc. Each collection has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the scenario.
We can use collection to work with a group of related objects that can dynamically grow or shrink when objects are added or deleted based on our needs.
Remember: The Non-generic collections are not strongly typed and store data as objects. So, retrieving the value from them involves boxing and unboxing.
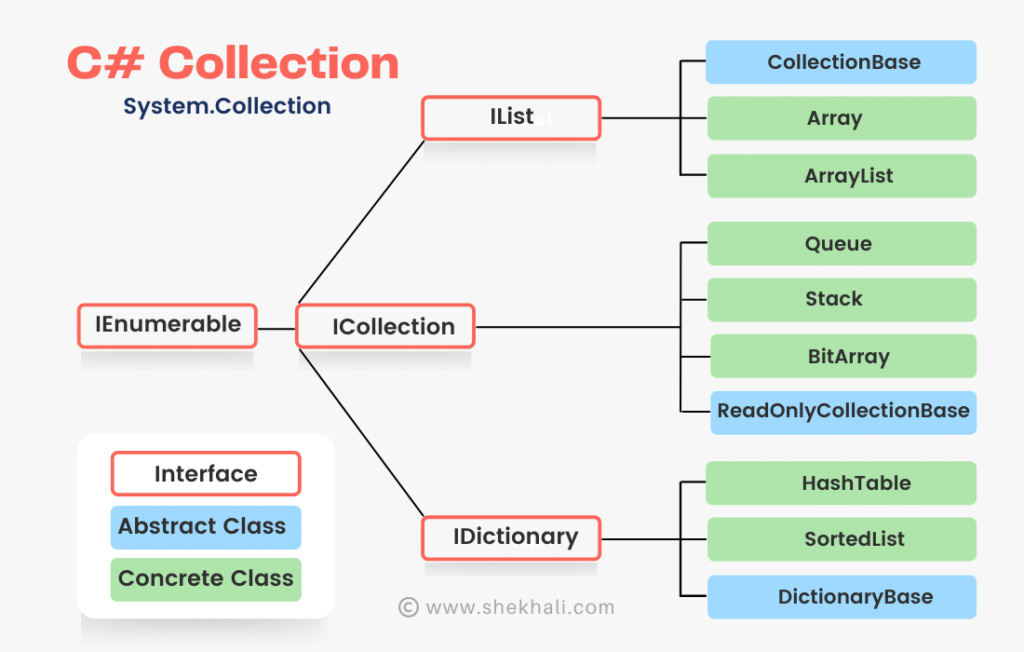
C# Collections Workflow
The Collections in C# are divided into several classes, some of which are represented in the picture below:
01. Queue in C#
A Queue is a collection that holds elements in a first-in, first-out (FIFO) order. Elements are added to the back of the queue and removed from the front. Queues are helpful when you need to process elements in the order in which they were stored.
The first element of the queue is the first one to be removed. Adding an item to a queue is called an enqueue, and removing an item is called a dequeue.
Here is an example of how to declare and initialize a queue named numberQueue of integers in C#:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace QueueExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new queue of integers
Queue<int> numberQueue = new Queue<int>();
// Enqueue elements into the queue
numberQueue.Enqueue(10);
numberQueue.Enqueue(20);
numberQueue.Enqueue(30);
numberQueue.Enqueue(40);
numberQueue.Enqueue(50);
// Display the elements in the queue
Console.WriteLine("Elements in the queue:");
foreach (int num in numberQueue)
{
Console.WriteLine(num);
}
// Dequeue elements from the queue
int dequeuedElement = numberQueue.Dequeue();
Console.WriteLine($"Dequeued element: {dequeuedElement}");
// Display the updated queue
Console.WriteLine("Elements in the queue after dequeue:");
foreach (int num in numberQueue)
{
Console.WriteLine(num);
}
}
}
}
Output:
Elements in the queue:
10
20
30
40
50
Dequeued element: 10
Elements in the queue after dequeue:
20
30
40
50The image below illustrates the sequential flow of the queue process in the C#.

C# Queue Declaration
In C#, you can use both generic and non-generic queue types to create object instances for Queue collections.
01. By using the namespace System.Collections.Generic
Queue<int> intQueue = new Queue<int>(); // Generic Queue02. By using the namespace System.Collections
Queue queueCollection = new Queue(); // Non Generic Queue02. Stack in C#
A Stack is a collection that contains elements in a last-in, first-out (LIFO) order. Elements are added to the top of the stack and removed from the top as well. Stacks are helpful when you need to process elements in the reverse order in which they were added.
Adding an item on top of the stack is called push and removing an item from the stack is called pop.
Here is an example of how to declare and initialize a stack of integers in C#:
Stack<int> numbers = new Stack<int>();
numbers.Push(1);
numbers.Push(2);
numbers.Push(3);
numbers.Push(4);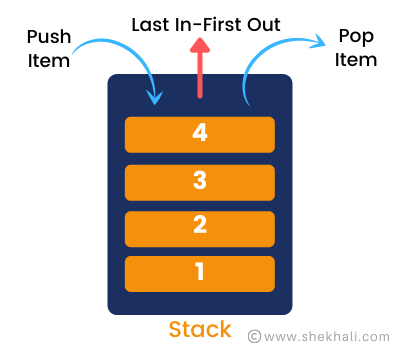
Example: Stack In C#
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace StackExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Stack stack = new Stack();
// Adding (Pushing) elements to the stack
stack.Push(1);
stack.Push(2);
stack.Push(3);
stack.Push(4);
stack.Push(5);
// Displaying stack elements
foreach (Object obj in stack)
{
Console.Write($" { obj }");
}
// Access Stack last (top-most) inserted element
Console.WriteLine($"\n Peek Element : {stack.Peek()}");
// Removing (Popping) an element from the stack
stack.Pop();
Console.WriteLine("\n Elements after pop operation");
foreach (Object obj in stack)
{
Console.Write($" { obj }");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
// Output:
// 54321
// Peek Element : 5
//Elements after pop operation
// 4321
}The following are the various commonly used methods used in Stack.
| C# Stack Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Push: | The Push method inserts an element at the top of the Stack collection. |
| Pop: | The Pop method removes an element from the top of the Stack collection and returns it. |
| Peek: | The Peek method returns an element from the top of the Stack without removing it. |
| Clear: | The Clear method is used to remove all the elements from the Stack. |
| Clone: | The Clone method creates a shallow copy of the Stack. |
| Contains: | The Contains method checks if the element is in the Stack. |
03. Arrays in C#
An Array is a fixed-size collection that stores elements of the same type in a contiguous memory location. These elements are organized in sequential order and can be accessed using numerical indices.
Arrays are helpful when you know the number of elements you need to store in advance.
Here is an example of how to declare and initialize an array of integers in C#:
using System;
namespace ArrayExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Declare an array of integers with a fixed size of 5
int[] numbers = new int[5];
// Initialize the array elements
numbers[0] = 10;
numbers[1] = 20;
numbers[2] = 30;
numbers[3] = 40;
numbers[4] = 50;
// Display the elements of the array
Console.WriteLine("Array elements:");
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(numbers[i]);
}
}
}
}
Output:
Array elements:
10
20
30
40
5004. Dictionary in C#
A Dictionary is a collection that holds key-value pairs. Each key in the dictionary maps to a value, which can be of any data type. Dictionaries are helpful when looking for a value based on its key.
Here is an example of how to declare and initialize a dictionary of strings and integers in C#:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DictionaryExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create a new dictionary to store student names and their corresponding ages
Dictionary<string, int> studentAges = new Dictionary<string, int>();
// Add key-value pairs to the dictionary
studentAges.Add("Krishna", 20);
studentAges.Add("Dhruv", 22);
studentAges.Add("Lakshmi", 19);
studentAges.Add("Shekh Ali", 25);
// Display the elements in the dictionary
Console.WriteLine("Student Ages:");
foreach (var kvp in studentAges)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{kvp.Key}: {kvp.Value}");
}
// Accessing a specific value using the key
string studentName = "Dhruv";
if (studentAges.ContainsKey(studentName))
{
int age = studentAges[studentName];
Console.WriteLine($"{studentName}'s age: {age}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($"{studentName} not found in the dictionary.");
}
}
}
}
Output:
Student Ages:
Krishna: 20
Dhruv: 22
Lakshmi: 19
Shekh Ali: 25
Dhruv's age: 2205. HashTable in C#
A Hashtable is a collection that stores key-value pairs of different data types in a hash table. The keys are hashed to produce a unique index in the table, which is used to look up the corresponding value. Hashtables are useful when you need to look up values based on their keys but don’t want to use a dictionary because they are not unique.
- The
Hashtablecan contain duplicate values but not duplicate keys. - Hashtable is a non-generic collection type available in the
System.Collectionsnamespace.
Key | A unique integer is used for indexing the value in the hashtable. |
Value | Data that is associated with the key. |
Here is an example of how to declare and initialize a Hashtable in C#:
C# HashTable Declaration
The following is the syntax to declare a Hashtable in C#.
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();C# HashTable Examples
The example below demonstrates how to create, initialize, and perform various actions on a Hashtable in C#.
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace HashTableExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Creating a hashtable variable
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
// Adding Country Codes
hashtable.Add("91", "India");
hashtable.Add("92", "Pakistan");
hashtable.Add("1", "United States");
hashtable.Add("33", "France");
hashtable.Add("61", "Australia");
// ContainsKey: to Check if key is available in the hashtable
if (hashtable.ContainsKey("91"))
{
Console.WriteLine(" Key (91) is available in the list");
}
// ContainsValue: to Check if value is available
if (hashtable.ContainsValue("India"))
{
Console.WriteLine(" Value (India) is available in the list");
}
// To remove an item from a hashtable based on its key.
hashtable.Remove("92");
// Getting the collection of the keys.
ICollection key = hashtable.Keys;
// Displaying the keys and values
foreach (string k in key)
{
Console.WriteLine($" {k} : { hashtable[k]}");
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
// Output:
// Key (91) is available in the list
// Value(India) is available in the list
// 33 : France
// 1 : United States
// 61 : Australia
// 91 : India
}The following are the various commonly used methods used in HashTable.
| C# Hashtable Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Add: | The Add method inserts an element with the specified key and value. |
| Remove: | The Remove method removes an element with a specified key from the Hashtable collection. |
| Clear: | The Clear method is used to remove all the elements from the Hashtable |
| Clone: | The Clone method creates a shallow copy of the Hashtable. |
| Contains: | The Contains method checks if the element is in the Hashtable. |
| ContainsKey: | The ContainsKey method determines whether the Hashtable contains a specific key or not. |
| ContainsValue: | The ContainsValue method determines whether the Hashtable contains a specific value or not. |
06. ArrayList in C#
ArrayList is the non-generic type of collection that is defined in the System.Collections namespace. It is a dynamic array that can hold the data of multiple data types. ArrayList is very similar to an array, but it can be dynamically grown or shrunk when objects are added or deleted based on our needs.
Example: C# ArrayList
The following is an example of an ArrayList in C# Programming.
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace ArrayListExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Creating an arraylist collection
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
// Adding elements in the ArrayList
arrayList.Add("Hello");
arrayList.Add(10);
arrayList.Add(20);
arrayList.Add(30);
arrayList.Add(40.5f);
arrayList.Add(60);
arrayList.Add(32);
// Removing element
arrayList.Remove(32);
//Creating new arraylist
ArrayList arrayList2 = new ArrayList() { "Shekh", "Ali" };
// Adding arrayList2 to existing arrayList
arrayList.AddRange(arrayList2);
// Inserting element into arraylist
arrayList.Insert(1, "World");
// Access elements by index Position
Console.WriteLine($"Element at Index 0:{arrayList[0]}");
// Count property
Console.WriteLine($"ArrayList Total Count:{arrayList.Count}");
// Accessing ArrayList Elements Using Foreach loop
foreach (object obj in arrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
// Removing an element at index 0 from ArrayList
arrayList.RemoveAt(1);
Console.WriteLine("** Removing 5 elements starting from index 1 **");
arrayList.RemoveRange(1, 5);
foreach (object obj in arrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(obj);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
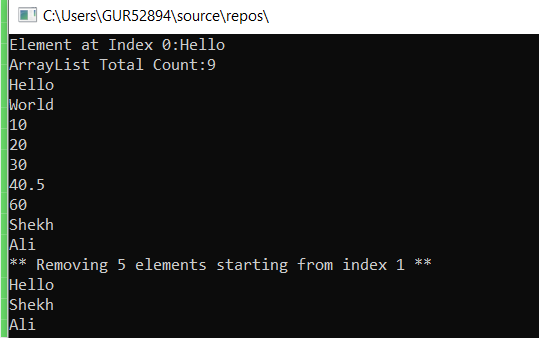
Following is the output of the above program of the ArrayList.
07. C# SortedList
The SortedList class represents a collection of key/value pairs that by default sort items by key in ascending order. A SortedList is a combination of an array and a hash table that allows you to access an element either by a key or an index. C# contains both generic and non-generic SortedList collections in System.Collections.Generic and System.Collections namespace respectively.
C# SortedList Characteristics
- A
SortedListkey must be unique and cannot be null. - A SortedList value can be null or duplicate.
- A non-generic
SortedListcomes underSystem.Collectionsnamespace. - The SortedList indexer accepts a key to return the value associated with it(Example: sortedList[key]).
Example: C# SortedList
using System;
using System.Collections;
namespace SortedListExample
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Creating SortedList
SortedList sortedList = new SortedList();
// Adding names in SortedList
sortedList.Add("01", "Shekh Ali");
sortedList.Add("02", "Kalpana");
sortedList.Add("03", "Priyanka");
sortedList.Add("04", "Robert");
sortedList.Add("05", "Minhaj Ali");
sortedList.Add("06", "Suhail Khan");
if (sortedList.ContainsValue("Shekh Ali"))
{
Console.WriteLine("This name is already in the SortedList");
}
else
{
sortedList.Add("07", "Shekh Ali");
}
// Getting keys collection.
ICollection keys = sortedList.Keys;
foreach (string key in keys)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{key} : {sortedList[key]}");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
//Output:
//This name is already in the SortedList
//01 : Shekh Ali
//02 : Kalpana
//03 : Priyanka
//04 : Robert
//05 : Minhaj Ali
//06 : Suhail Khan
}
}FAQs
Q: What are collections in C#?
Collections in C# are a predefined set of classes in the System.Collections namespace to store multiple items in a single unit.
Collections are used to work with a group of related objects that can dynamically grow or shrink when objects are added or deleted based on our needs.
Q: What is the difference between collection and array?
Arrays are fixed in size, which means that once you create an array, you will not be able to resize it to meet your needs.
Collections, on the other hand, are growable. They can dynamically grow or shrink when objects are added or deleted as needed.
Q: Is ArrayList a generic collection in C#?
In C#, an ArrayList is a collection of non-generic objects that can increase in size dynamically. While similar to an array, it differs in its capability to adjust its size as necessary. This feature makes ArrayList useful as it allows programmers to include data of any data type without prior knowledge of the type or size.
Q: What is the difference between Array and Arraylist Collections in C#?
The size of an Array is fixed and cannot be changed dynamically. On the other hand, the size of an ArrayList can be dynamically changed when items are added or deleted.
Array class is available in System.Array namespace, whereas ArrayList belongs to the System.Collections namespace.
Q: How many types of collections are there in C#?
There are two types of collections available in C#: non-generic and generic collections.
The non-generic collection types are available in System.Collections namespace while generic collection types are available in System.Collections.Generic namespace.
Q: Why do we use collections in C#?
We use collections in C# to efficiently manage and organize groups of data or objects. Collections help us store multiple items together in a structured way, making it easier to perform operations like adding, removing, searching, sorting, and iterating through the elements.
Q: How do I choose the right collection for my program?
It depends on what you need to do with your data. If you need fast lookups, go for a dictionary. For a flexible list, use a list. Queues or stacks might be best if you need to manage items in a specific order.
Q: How are queues and stacks useful in C# collections?
Queues are like lines where people wait in order. The first one in is the first one out (FIFO). Stacks are like piles of plates. The last one put on is the first one taken off (LIFO). They’re great for managing things in a specific order.
References MSDN: Collections (C#)
Thank you for taking the time to read the blog about “Collections in C#“, if you find it interesting, please put your comment, and share it with others. Thanks.
You Might Like:
- C# Tutorial
- C# Stack
- C# Dictionary with Examples
- C# List Class With Examples
- C# Abstract class Vs Interface
- C# Array vs List: When should you use an array or a List?
- Generic Delegates in C# With Examples
- C# Hashtable vs Dictionary vs Hashset
- Constructors in C# with Examples
- C# Enum | How to Use enumeration type in C#?
- Properties In C# with examples
- C# Event with examples
- Multithreading in C#
- IEnumerable Interface in C# with examples
- C# Monitor class in multithreading
- C# Struct vs Class
- Difference Between Array And ArrayList In C#: Choosing the Right Collection - May 28, 2024
- C# Program to Capitalize the First Character of Each Word in a String - February 21, 2024
- C# Program to Find the Longest Word in a String - February 19, 2024