Triggers in SQL are special types of stored procedures that are automatically executed in response to specific events or changes within a database. In this article, we will explore triggers in SQL and provide a trigger example in SQL Server to help you understand how they work.
Table of Contents
- 1 What are Triggers in SQL?
- 2 Advantages of Triggers in SQL
- 3 When to use Triggers in SQL
- 4 Trigger Example in SQL Server
- 5 Types of triggers in SQL
- 6 Limitations of triggers In SQL Server
- 7 Conclusion:
- 8 FAQ
What are Triggers in SQL?
Triggers are database objects that are associated with a table or view and are automatically executed when specific actions occur. These actions can be any of the following:
- INSERT
- UPDATE
- DELETE
- TRUNCATE
SQL triggers are used to enforce business rules, keep data clean, and enforce referential constraints. They are used to implement security measures and perform audit trails on the data.
Advantages of Triggers in SQL
There are several benefits to using triggers in SQL, including:
- Automate Complex Processes: Triggers can be used to automate complex processes and reduce the need for manual intervention.
- Improved data integrity: SQL triggers can enforce business rules and maintain data integrity by preventing unauthorized data changes by the user.
- Improved performance: Triggers in SQL can help you to improve performance by reducing the need for manual processes and the amount of code required to maintain data integrity.
- Security: Triggers can also be used to enforce security measures by preventing unauthorized data access.
When to use Triggers in SQL
Triggers are most useful when a complex business process needs to be automated. For eg, if you want to keep track of all changes made to a specific table then you could use a trigger to automatically record the changes in a separate audit table.
Another example is when you need to enforce business rules. A trigger, for example, could be used to prevent users from deleting data in a specific table.
Syntax:
CREATE TRIGGER tr_audit_insert
ON dbo.YourTable
AFTER INSERT
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO dbo.AuditTable (Column1, Column2, Column3)
SELECT Column1, Column2, Column3
FROM inserted;
END
Trigger Example in SQL Server
To demonstrate the use of triggers, let’s consider a scenario where we have a table called Orders and we want to keep track of all changes to the data in this table.
First, let’s create the Orders table:
CREATE TABLE Orders (
OrderID INT PRIMARY KEY,
CustomerID INT,
OrderDate DATE,
TotalAmount DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
Now, let’s insert some sample data into the Orders table:
INSERT INTO Orders (OrderID, CustomerID, OrderDate, TotalAmount)
VALUES (1, 1001, '2022-01-01', 1000),
(2, 1002, '2022-02-01', 2000),
(3, 1003, '2022-03-01', 3000),
(4, 1004, '2022-04-01', 4000);
Let’s run the following SELECT query to see the data of the Orders table.
SELECT * from orders;
| OrderID | CustomerID | OrderDate | TotalAmount |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1001 | 2022-01-01 | 1000 |
| 2 | 1002 | 2022-02-01 | 2000 |
| 3 | 1003 | 2022-03-01 | 3000 |
| 4 | 1004 | 2022-04-01 | 4000 |
Now that we have the Orders table and sample data, let’s create a DML trigger that will keep track of all changes to the data in this table:
-- Create TRIGGER
CREATE TRIGGER tr_AuditOrders
ON Orders
AFTER INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @EventType VARCHAR(20)
SET @EventType =
CASE
WHEN EXISTS (SELECT * FROM inserted) AND EXISTS (SELECT * FROM deleted) THEN 'UPDATE'
WHEN EXISTS (SELECT * FROM inserted) THEN 'INSERT'
WHEN EXISTS (SELECT * FROM deleted) THEN 'DELETE'
END
IF @EventType = 'DELETE'
BEGIN
INSERT INTO AuditOrders (EventType, EventTime, OrderID, CustomerID, OrderDate, TotalAmount)
SELECT @EventType, GETDATE(), OrderID, CustomerID, OrderDate, TotalAmount
FROM deleted;
END
ELSE
BEGIN
INSERT INTO AuditOrders (EventType, EventTime, OrderID, CustomerID, OrderDate, TotalAmount)
SELECT @EventType, GETDATE(), OrderID, CustomerID, OrderDate, TotalAmount
FROM inserted;
END
END;
Code Explanation:
In this example, the trigger tr_AuditOrders is created on the Orders table and will be executed after an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement is executed. The inserted and deleted virtual tables are used to retrieve the data that was affected by the DML operation. The type of event that triggered the trigger (INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE) is determined based on the existence of data in the inserted and deleted tables. The event type, time, and affected data are then inserted into the AuditOrders table.
Let’s create the AuditOrders table to store the audit data:
CREATE TABLE AuditOrders (
EventType VARCHAR(20),
EventTime DATETIME,
OrderID INT,
CustomerID INT,
OrderDate DATE,
TotalAmount DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
Now, let’s test the trigger by inserting, updating, and deleting data in the Orders table:
-- Insert new record
INSERT INTO Orders (OrderID, CustomerID, OrderDate, TotalAmount)
VALUES (5, 1005, '2022-05-01', 5000);
-- Update record
UPDATE Orders
SET TotalAmount = TotalAmount + 1000
WHERE OrderID = 5;
-- Delete record
DELETE FROM Orders
WHERE OrderID = 5;
Let’s query the AuditOrders table to see the audit data that was generated by the trigger:
SELECT * FROM AuditOrders;
This query will show the event type, time, and data that was affected by the DML operations on the Orders table.
Here is an example of what the results of this query might look like:
AuditOrders Table:
| EventType | EventTime | OrderID | CustomerID | OrderDate | TotalAmount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INSERT | 2023-02-09 20:20:57.890 | 5 | 1005 | 2022-05-01 | 5000.00 |
| UPDATE | 2023-02-09 20:20:57.900 | 5 | 1005 | 2022-05-01 | 6000.00 |
| DELETE | 2023-02-09 20:20:57.900 | 5 | 1005 | 2022-05-01 | 6000.00 |
Types of triggers in SQL
In SQL, there are two main types of triggers: DDL (Data Definition Language) triggers and DML (Data Manipulation Language) triggers.
01. DDL Triggers
DDL triggers in SQL are used to track database schema changes such as the creation or modification of tables, views, or stored procedures. DDL triggers are commonly used for auditing and security purposes because they allow you to track who and what changes are being made to the database.
DDL triggers are fired in response to CREATE, ALTER, and DROP statements in SQL.
Here is an example of a DDL trigger in the SQL Server:
CREATE TRIGGER tr_audit_ddl
ON DATABASE
FOR CREATE_TABLE
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO dbo.AuditTable (EventType, EventTime, ObjectName)
VALUES ('CREATE_TABLE', GETDATE(), OBJECT_NAME(@@PROCID));
END
In this example, The trigger is created on the database and will be executed whenever a CREATE TABLE statement is executed.
The @@PROCID function returns the ID of the stored procedure that caused the event. The event type and time, as well as the name of the newly created object, are then inserted into the dbo.AuditTable table.
02. DML Triggers
DML triggers are used to track changes to data within a table, such as INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE operations. DML triggers are typically used for maintaining data integrity and enforcing business rules.
In the above examples, we have already created a DML trigger tr_AuditOrders in SQL Server:
How To Create SQL Server Trigger For Update Event?
Let’s create a SQL server trigger for an update event that will get executed once a row is updated in a table.
Before creating a trigger, let’s first create sample tables for examples. Let’s create a table “tblEmployee” to keep employee personnel information and a table “tblEmployeeHistory” to contain each modified record.
SQL Server Script To Create “tblEmployee” Table
-- Creating a new table "tblEmployee"
CREATE TABLE tblEmployee
(
[Id] INT PRIMARY KEY,
[Name] NVARCHAR(30),
[Gender] VARCHAR(10),
[City] VARCHAR(50),
[DeptId] INT
)
-- Inserting data into the "tblEmployee" table.
INSERT INTO tblEmployee VALUES
(101,'Shekh Ali','Male','Delhi', 1),
(102,'Mark Adam','Male','New York', 1),
(103,'Julie Folden','Female','Chicago', 2);
-- SQL Script to create a table "tblEmployeeHistory"
CREATE TABLE tblEmployeeHistory
(
[Id] INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
[AuditData] NVARCHAR(500),
[Date] DATETIME
)
-- Select records from the following tables
SELECT * FROM tblEmployee;
SELECT * FROM tblEmployeeHistory;
After executing the SQL statements referred to above, the following tables will be created in the database.
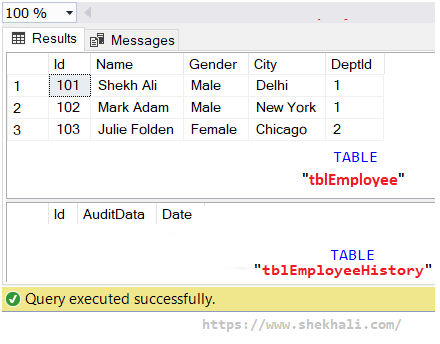
In general, DML triggers create two special (virtual) magic tables called INSERTED and DELETED with the same structure or scheme as their base table.
The INSERTED table contains newly inserted records; however, the DELETED table contains old records after updating or deleting rows in a specific table.
In the SQL server trigger for the update, the temporarily inserted and deleted tables are created.
Syntax: SQL Trigger For Update Query
-- SQL script for creating a DML trigger for update events.
-- Author: Shekh Ali
CREATE TRIGGER TR_TblEmployee_ForUpdate ON tblEmployee
FOR UPDATE
AS
BEGIN
-- Declare variables to hold the old and updated record
DECLARE @Id INT, @OldDeptId INT;
DECLARE @OldName NVARCHAR(30), @OldGender NVARCHAR(10), @OldCity NVARCHAR(30);
-- Variable to build the audit string
DECLARE @AuditString NVARCHAR(1000);
-- Select the corresponding Id from the inserted table
Select Top 1 @Id = Id FROM INSERTED;
-- Select the corresponding row from the deleted table
SELECT @OldName = Name, @OldGender = Gender,
@OldCity = City, @OldDeptId = DeptId
FROM DELETED WHERE Id = @Id;
-- Build the audit string dynamically
Set @AuditString = 'Employee with Id = ' + Cast(@Id as NVARCHAR(4)) + ' changed'+
+' Name: ' +@OldName +' Gender: ' +' City: '+@OldCity +' DeptId: '+ Cast(@OldDeptId as NVARCHAR(4));
INSERT INTO tblEmployeeHistory VALUES(@AuditString, getdate());
END
Steps to create SQL update trigger
-
- First, To create a trigger, use the CREATE TRIGGER keywords, then specify the unique trigger name (Example: TR_TblEmployee_ForUpdate).
- Second, the options FOR, INSTEAD OF, or AFTER specify when the trigger will be executed either before or after single or multiple rows are modified.
- Then use the keyword ON to specify the name of the table associated with the trigger.
- Finally, specify the trigger body started from AS BEGIN to END which contains one or more SQL statements to be executed once trigger fired.
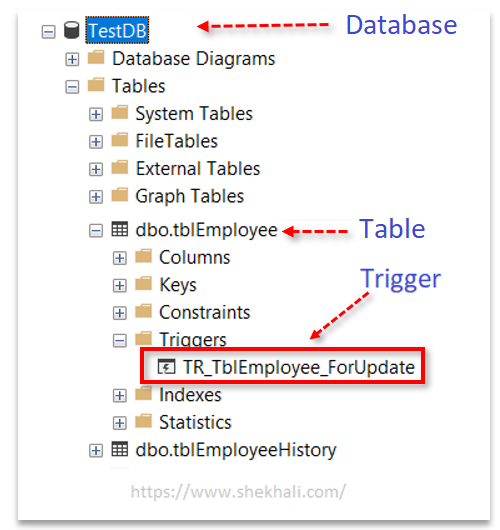
After execution of the above-mentioned SQL statements, a new SQL trigger for an update command will be created in the table-level trigger directory.
Please see the below image for reference.
Update record in a database table
Let’s try to update a record in the “tblEmployee” table.
-- Update query
UPDATE tblEmployee SET City='Mumbai' WHERE Id=101;
Immediately after executing the UPDATE statement, the AFTER UPDATE trigger launches, and the new and old data will be stored in the INSERTED and DELETED magic tables.
Now we will be able to see the updated record in the”tblEmployee” table and the old record in the “tblEmployeeHistory” table inserted by the after update trigger.
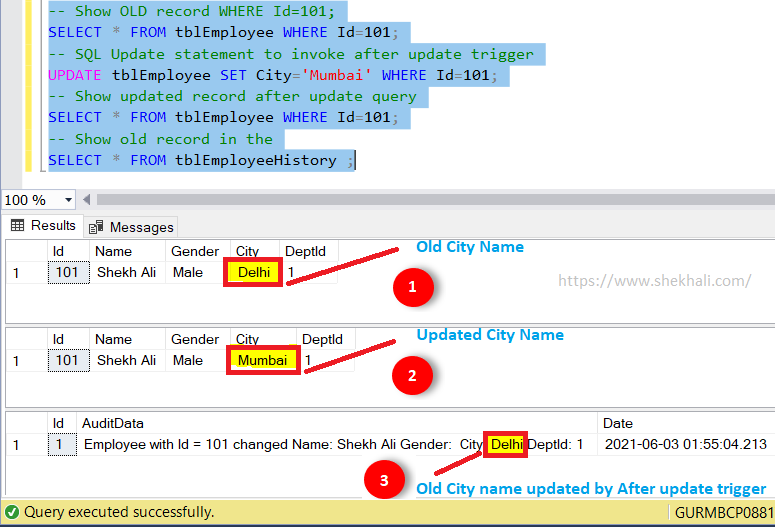
How To Create SQL Server Instead Of Update Trigger?
In SQL Server, the INSTEAD OF UPDATE Trigger is executed automatically instead of the actual UPDATE event on a table or a view.
Suppose we have an INSTEAD OF UPDATE trigger on a table “tblEmployee”.
When we attempt to update a row of the “tblEmployee” table, the following trigger will be executed automatically instead of the actual Update event.
Let’s put one condition inside the trigger, if someone tries to update the Id column from the “tblEmployee” table, then the such record must not be allowed to update but raised an error message.
The update query will be only allowed to execute If any other columns are updated rather than the ID column.
Syntax: SQL Instead of update trigger
Following are the SQL statements used to create Instead of update triggers.
-- SQL script to create Instead Of Trigger.
-- Author: Shekh Ali
CREATE TRIGGER [dbo].[Tr_tblEmployee_InsteadOfUPDATE]
ON [dbo].[tblEmployee]
INSTEAD OF UPDATE
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @EmployeeId INT,@DeptId INT
DECLARE @Name VARCHAR(50), @City VARCHAR(50), @Gender VARCHAR(50)
SELECT @EmployeeId = Id,
@Name = [Name],
@City = City,
@Gender = Gender,
@DeptId = DeptId
FROM INSERTED ;-- Magic Table
IF UPDATE(Id)
BEGIN
RAISERROR('EmployeeId cannot be updated.', 16 ,1)
ROLLBACK
INSERT INTO tblEmployeeHistory
VALUES( 'EmployeeId ' + Cast(@EmployeeId as NVARCHAR(5)) + ' cannot be updated.',GETDATE())
END
ELSE
BEGIN
UPDATE [tblEmployee]
SET [Name] = @Name,
City = @City,
Gender = @Gender,
DeptId = @DeptId
WHERE Id = @EmployeeId
END
END
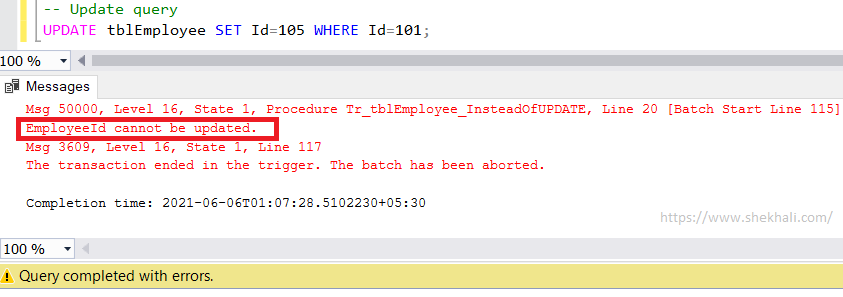
Let’s try to update the Id column in the table “tblEmployee”.
-- Update query
UPDATE tblEmployee SET Id=105 WHERE Id=101;
The following error message will be shown when the Id field is updated in the tblEmployee table.
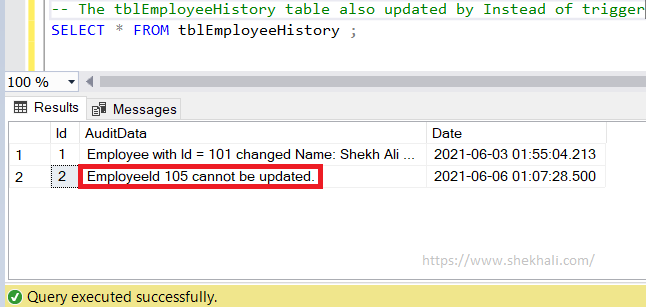
The “tblEmployeeHistory” table is also updated through the SQL Instead of Update trigger
Example: SQL For Insert Trigger
Create an INSERT trigger that will add the newly added employee Id to the History table.
-- SQL FOR INSERT TRIGGER EXAMPLE
CREATE TRIGGER [dbo].[Tr_tblEmployee_INSERT]
ON [dbo].[tblEmployee]
FOR INSERT
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @EmployeeId INT
SELECT @EmployeeId = INSERTED.Id
FROM INSERTED
INSERT INTO tblEmployeeHistory
VALUES( 'EmployeeId ' + Cast(@EmployeeId as NVARCHAR(5))
+ ' Inserted.',GETDATE())
END
Let’s try to insert the following employee record into the “tblEmployee” table.
INSERT INTO tblEmployee VALUES (104,'Rajat Sharma','Male','Delhi', 1);
Once we execute the above Insert statement, the trigger will insert the employee id detail in the tblEmployeeHistory table.
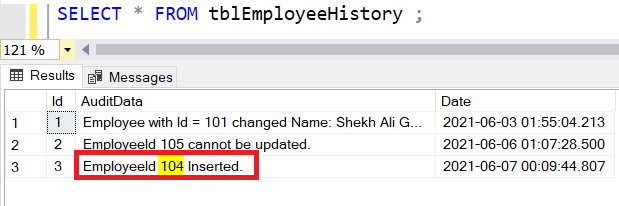
How to Create Delete Trigger In SQL Server?
Let’s Create a trigger that will not allow the Delete operation on the table “tblEmployee”.
CREATE TRIGGER Tr_tblEmployee_Delete
ON tblEmployee
FOR DELETE
AS
BEGIN
PRINT 'DELETE OPERATION IS RESTRICTED.'
ROLLBACK TRANSACTION
END
Let’s try to DELETE the record of the employee with Id is 101 in the table “tblEmployee”.
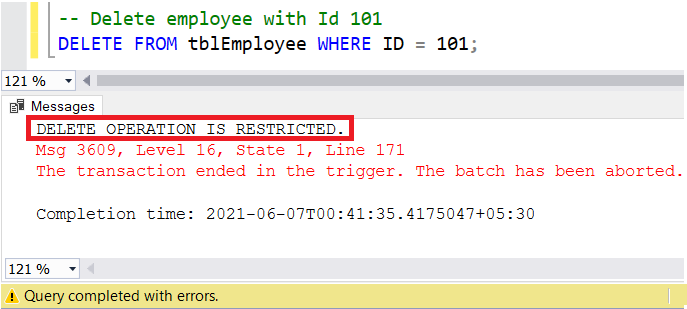
-- Delete employee with Id 101
DELETE FROM tblEmployee WHERE ID = 101;
When we try to execute the above Delete statement, it gives us the following error.
Limitations of triggers In SQL Server
- CREATE TRIGGER must be the first statement in the batch and can apply to only one table.
- A trigger is created only in the current database; however, a trigger can reference objects outside the current database.
- If the trigger schema name is specified to qualify the trigger, qualify the table name in the same way.
- The same trigger action can be defined for more than one user action (for example, INSERT and UPDATE) in the same CREATE TRIGGER statement.
INSTEAD OF DELETE/UPDATE triggers can’t be defined on a table that has a foreign key with a cascade on DELETE/UPDATE action defined.
Conclusion:
In this article, we provided a comprehensive overview of triggers in SQL Server, including a trigger example in SQL. We also demonstrated how to implement triggers in SQL Server, and outlined the advantages of using triggers in your database.
FAQ
Q: What are triggers and their types in the SQL server?
A trigger in an SQL Server is a special kind of stored procedure that is triggered automatically when a given event such as Insert, Update, or Delete occurs against a table in a database.
Types of Triggers
1. Data Definition Language (DDL) triggers: CREATE, ALTER, DROP
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML) triggers: INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE
3. CLR triggers
4. and Logon triggers
Q: What is after trigger in SQL Server?
The AFTER triggers in the SQL server are executed once the INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE command is successfully executed on the database object.
Q: Can triggers update views in SQL Server?
Yes, the View can be updated by using Instead of trigger in the view.
Q: How do I disable a specific trigger in SQL?
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE TableName DISABLE TRIGGER TriggerName;
Example:
ALTER TABLE tblEmployee DISABLE TRIGGER Tr_tblEmployee_Delete;
Q: How do I enable a specific trigger in SQL?
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE TableName ENABLE TRIGGER TriggerName;
Example:
ALTER TABLE tblEmployee ENABLE TRIGGER Tr_tblEmployee_Delete;
References: MSDN- CREATE TRIGGER (MSDN)
You might also like:
- Having VS Where Clause in SQL
- Group by Month in SQL: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples in SQL Server
- Delete vs Truncate vs Drop in SQL Server
- UNION vs UNION ALL in SQL SERVER
- Different ways to delete duplicate rows in SQL Server
- Types of Joins in SQL Server
- Function vs Stored procedure in SQL Server
- Stored Procedure in SQL Server With Examples
- Create, Alter, and Drop Database In SQL Server
- SQL Comparison Operators (Less than, Greater than, Equal, Not Equal operators)
- Primary Key Constraint In SQL Server
- View In SQL | Types Of Views In SQL Server
- SQL Server Trigger Update, Insert, Delete Examples
- SQL pivot tables
Don’t keep this post to yourself, share it with your friends and let us know what you think in the comments section.
- C# 12 New Features in 2025: What’s New with .NET 8 - April 11, 2025
- Difference Between WCF and Web API with Examples: A Comprehensive Guide - March 27, 2025
- PUT vs PATCH vs POST in REST API: Key Differences Explained With Examples - March 23, 2025