In C#, the key difference between abstraction and encapsulation is that encapsulation wraps data and methods into a single unit called class, whereas abstraction hides implementation details and just shows users the functionality.
Table of Contents
- 1 What is the difference between abstraction and encapsulation in C# programming?
- 2 Definition of Abstraction in C#
- 3 How to Achieve Abstraction in C#?
- 4 Encapsulation in C#?
- 5 Key points about encapsulation
- 6 How to Achieve encapsulation in C#?
- 7 Difference between Abstraction and Encapsulation in C#
- 8 Abstraction example
- 9 FAQs:
- 9.1 Q: Is there a difference between abstraction and abstract class?
- 9.2 Q: How do you achieve abstraction in C#?
- 9.3 Q: What is an abstraction, and how can you describe it with an example?
- 9.4 Q: What is the main difference between encapsulation and abstraction in C#?
- 9.5 Q: How are Abstraction and Encapsulation related?
- 10 Conclusion
What is the difference between abstraction and encapsulation in C# programming?
Abstraction: Abstraction is the concept of hiding the complex implementation details and showing only the necessary information to the outside world. It defines what an object should do without exposing how it achieves its purpose.
- It allows you to define a blueprint for a class without specifying the implementation details.
- Abstraction can be achieve through abstract classes and interfaces in C#.
Code Example of Abstraction in C#:
// Abstract class
public abstract class Shape
{
// Abstract method
public abstract void Draw();
}
// Concrete class implementing the abstract class
public class Circle : Shape
{
// Implementing the Draw method
public override void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("Drawing a circle");
}
}
Abstraction Example: Think of the outer layout of a Phone – The display screen is an important feature that represents the necessary functionality without exposing the internal mechanics.
Encapsulation: Encapsulation is the concept of bundling the data (variables) and methods (functions) that operate on the data into a single unit (class).
- It helps control access to data by hiding an object’s internal state and exposing only the necessary functionalities.
- Encapsulation can be achieve through access modifiers like private, protected, and public in C#.
- It wraps data and methods into a single unit (class), ensuring that clients interact with public properties rather than directly accessing private data.
Code example of encapsulation in C#:
public class Employee
{
// Private fields
private string name;
private int age;
// Public property for Name
public string Name
{
get { return name; }
set { name = value; }
}
// Public property for Age
public int Age
{
get { return age; }
set
{
if (value >= 18)
{
age = value;
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Age must be 18 or older.");
}
}
}
}
Code Explanation:
- Private fields: The
nameandagefields are declared as private, ensuring they cannot be accessed directly from outside theEmployeeclass. - Public properties: Instead of separate getter and setter methods, properties are used to encapsulate access to the private fields. This provides a cleaner syntax for getting and setting the values of
nameandage. - Name property: The
Nameproperty encapsulates access to thenamefield. It has both a getter and a setter, allowing external code to get and set the value ofname. - Age property: The
Ageproperty encapsulates access to theagefield. It also has both a getter and a setter. The setter includes logic to ensure that the new age is 18 or older before setting the value. If the age is not valid, it outputs an error message to the console.
Example: Imagine the inner implementation details of a Phone – the complex connections between display screens using circuits. Encapsulation shields these details from external users.
In short, Abstraction focuses on hiding the implementation details, while encapsulation focuses on bundling data and methods together and controlling access to the data. Both
concepts are important in object-oriented programming and help in creating more maintainable and scalable code
Definition of Abstraction in C#
Abstraction is the technique of exposing only the essential details while hiding the rest. In simple words, data abstraction is defined in C# as the process of reducing an object to its core and exposing only the relevant details of the object to the users.
“Abstraction is the process of working with ideas rather than putting them into action.
The implementation complexities are hidden from the users in abstraction.“
How to Achieve Abstraction in C#?
- In C#, we can use Abstract classes and interfaces to achieve Abstraction.
Complete abstraction is possible with interfaces that allow you to entirely encapsulate the implementation. - Abstract classes allow partial or complete abstraction because they might have concrete methods with implementation, resulting in partial abstraction.
Encapsulation in C#?
Encapsulation is a fundamental concept in object-oriented programming that involves bundling data (variables) and methods (functions) that operate on the data into a single unit (class) and controlling access to that data.
Encapsulation allows an object’s internal state to be hidden from the outside world, with access to the data restricted to designated methods within the class.
It promotes data hiding by encapsulating related functionalities within a class and providing a well-defined interface for interacting with the object.
Key points about encapsulation
Encapsulation in C# is a fundamental object-oriented programming (OOP) concept that refers to hiding an object’s implementation details from other parts of the program. It involves bundling the data (fields, properties) and behavior (methods) that operate on that data within a single unit called a class.
The class exposes a set of well-defined public interfaces (methods, properties, events) that other parts of the program can use to interact with the object while keeping the implementation details hidden. It provides several benefits, including:
Read my previous article to learn more about Encapsulation in C#.
How to Achieve encapsulation in C#?
In C#, encapsulation can be achieve using access modifiers such as private, public, protected, and internal to control the visibility of the members of a class.
By default, the access level of a member is private, meaning that it can only be accessed within the same class. On the other hand, Public members can be accessed from any part of the program.
In C#, encapsulation can be performed by:
- Declaring class variables as private.
- Providing a public method or a getter and setter property that can be used to modify and read the values of private variables.
“Encapsulation refers to a situation in which a class’s variables or data are hidden from other classes and can only be accessed through member functions/properties of the class in which they are specified.“
Let’s take a look at the code to see how encapsulation is implemented:
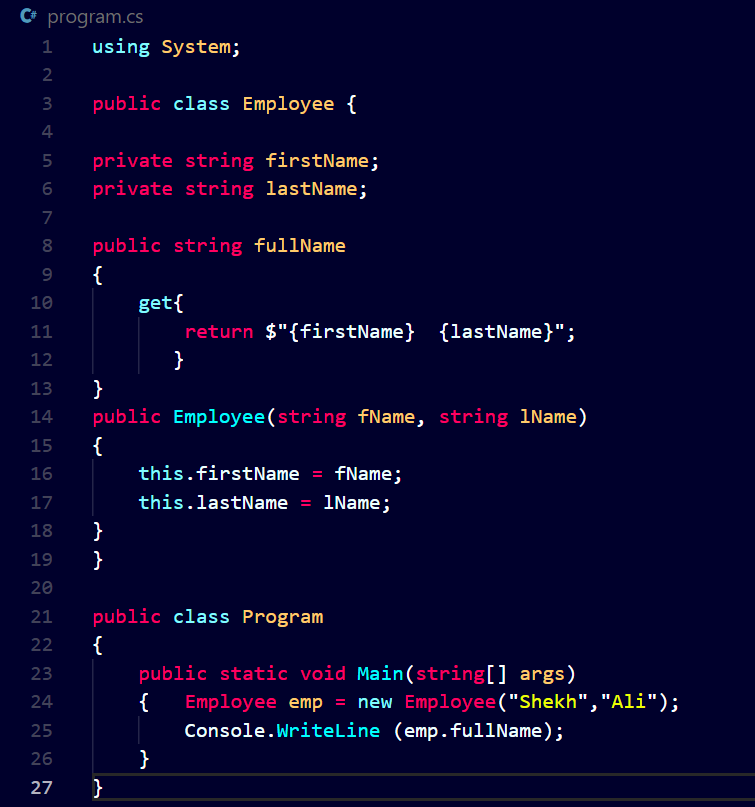
As you can see in the above code, we have created a class Employee with private variables firstName and lastName.
Then, we created a public property fullName to get the value from the private variables. Because private fields cannot be accessed outside of the class, any class wishing to get the employee name (private field value) must use this public property.
It allows us to quickly get the employee`s full name without worrying about how the Employee class handles first and last names internally.
Advantages of Encapsulation:
Here are some advantages of encapsulation in C#:
1. Data Hiding:
Encapsulation allows you to hide the internal state of an object by making data members private and providing public methods to access and modify that data. It helps prevent unauthorized access and manipulation of data, enhancing security and integrity.
2. Modularity:
Encapsulation promotes modularity by bundling data and methods together within a class. This makes managing and maintaining code easier, as related functionalities are grouped together, improving code readability.
3. Code Reusability:
Encapsulation facilitates code reusability by encapsulating common functionalities within a class. Other parts of the program can then interact with the class through its public interface, allowing for easy code reuse without duplicating it.
4. Flexibility and Maintenance:
Encapsulation enhances flexibility and maintenance of code by isolating the implementation details of a class. Changes to the internal implementation can be made without affecting other parts of the program, reducing the risk of unintended side effects and making it easier to update and maintain the codebase.
Refer this link to learn more about the Encapsulation in C#
Difference between Abstraction and Encapsulation in C#
| Abstraction | Encapsulation |
|---|---|
| 1. Abstraction is a technique for hiding unnecessary information. | Encapsulation, on the other hand, is a way of hiding data in a single unit called Class as well as a method of protecting information from the outside. |
| 2. Abstract classes and interfaces can be used to implement abstraction. | Encapsulation, on the other hand, can be implemented utilizing access modifiers such as private, protected, and public. |
| 3. Abstraction solves a problem at the design level. | whereas Encapsulation solves an issue at the implementation level. |
| 4. Abstraction is used to hide something, but to a greater extent (class, interface). Clients who use an abstract class (or interface) are only interested in knowing what it can do, not what it was. | Encapsulation hides private variables or implementations in a class that are frequently modified to prevent outsiders from accessing them directly. We must use the getter and setter methods of a property to access them. |
| 5. Abstraction emphasizes what should be done. | whereas encapsulation emphasizes how it should be done. |
| 6. The class that implements the abstraction can be used as a parent class, with the child class inheriting its functionality, increasing reusability and reducing duplication. | Encapsulation allows the programmer to have more control over the data’s accessibility and transparency. |
Abstraction example
The following is a code snippet for data abstraction:
using System;
namespace AbstractionExample
{
/* C# program written to calculate the area
of a Circle and square using the concept of
data abstraction */
// Abstarct class
abstract class Shape
{
// Abstract method
public abstract double area();
}
// Child class( Circle) inheriting
// the parent (Shape) class.
class Circle : Shape
{
// private data member
private double radius;
// Constructor
public Circle(double radius)
{
this.radius = radius;
}
// overriding of the abstract method using the override keyword.
public override double area()
{
return (3.14 * radius * radius);
}
}
class Square : Shape
{
private double side;
public Square(double side)
{
this.side = side;
}
public override double area()
{
return (side * side);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Creating reference of Parent (Shape) class
// which refer to child (Circle & Square) classes instance.
Shape shape = new Circle(5.0);
Console.WriteLine($"Area of Circle = {shape.area()}");
shape = new Square(5.5);
Console.WriteLine($"Area of Square = {shape.area()}");
Console.ReadLine();
//Output:
//Area of Circle = 78.5
//Area of Square = 30.25
}
}
}
The Base class only exposes the method definition, input parameters, and return type of the abstract method. However, it does not expose the method`s implementation details, such as how it is implemented differently in different child classes; this is referred to as abstraction.
FAQs:
Q: Is there a difference between abstraction and abstract class?
Ans: Many people are puzzled by the terms abstraction and abstract class, Are they related?
Well, an abstract class differs from abstraction in that it is created with the goal of being implemented in a child class or subclass. Abstraction simply hides the data and reveals only the essential data by using access specifiers like public, protected, and private.
Q: How do you achieve abstraction in C#?
Ans: In C#, abstraction can be achieved by abstract classes and interfaces.
Q: What is an abstraction, and how can you describe it with an example?
Ans: In simple terms, abstraction hides unnecessary information and only shows the relevant attributes of an object.
For example, when driving a car, we are just concerned with driving the car, such as starting/stopping the car, accelerating/braking, and so on. We are unconcerned about the internal operation of the start/stop mechanism or the accelerate/brake process. We are simply uninterested in such technicalities.
Q: What is the main difference between encapsulation and abstraction in C#?
Encapsulation in C# is an OOP concept that encapsulates data and methods in a single unit known as class. On the other hand, abstraction in C# is an OOP concept that hides the implementation details and exposes only the functionality to the user.
They go hand in hand. Abstraction simplifies what an object does, while encapsulation ensures that its implementation details remain hidden. Together, they make code more organized and maintainable.
Conclusion
In this post, we have gone through the relevance of the OOPs concept and learned what abstraction and encapsulation mean. We went over several abstraction and encapsulation examples. We also discussed the advantages of abstraction and encapsulation. Finally, we looked at the difference between abstraction and encapsulation.
Thank you for reading the blog; if you enjoyed it, please like, comment, and share it with others.
References: C# | Abstraction
Articles to Check Out:
- C# Abstract class Vs Interface
- C# Encapsulation: Everything You Need to Know
- WCF vs WEB API
- Top 50 C# Interview Questions And Answers For Freshers And Experienced
- Collections in C# .NET
- ASP.NET Core Middleware With Examples
- C# Struct vs Class
- C# StreamReader & StreamWriter
- Boxing and Unboxing – C# Programming
- SOLID Design Principles in C#: A Complete Example
- Singleton Design Pattern in C#: A Beginner’s Guide with Examples
- C# Dependency Injection
- C# 12 New Features in 2025: What’s New with .NET 8 - April 11, 2025
- Difference Between WCF and Web API with Examples: A Comprehensive Guide - March 27, 2025
- PUT vs PATCH vs POST in REST API: Key Differences Explained With Examples - March 23, 2025