Polymorphism is a Greek word that means “many-shaped” or multiple forms of an object. You can use polymorphism in case you want to have multiple forms of one or more methods of a class with the same name.
Polymorphism is one of the main key concepts of object-oriented programming after encapsulation and inheritance.
In this article, we are going to learn about the different types of polymorphism in C#, how they work, how to implement them, and how to use polymorphism in our program code.
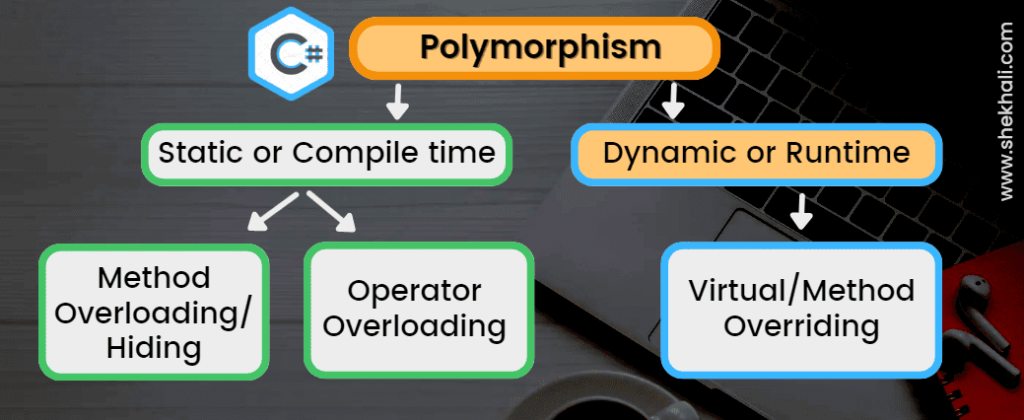
Table of Contents
- 1 Types of polymorphism in C#
- 2 01. Compile Time Polymorphism
- 3 02. Dynamic / Runtime Polymorphism
- 4 Rules for method overriding
- 5 FAQs
- 5.1 Q: How many different types of polymorphism are there in C#?
- 5.2 Q: What is dynamic or runtime polymorphism in C#?
- 5.3 Q: What is the main difference between overriding and overloading?
- 5.4 Q: What is the purpose of polymorphism in C#?
- 5.5 Q: Can you give a good example of polymorphism?
- 5.6 Q: What is the ‘virtual’ keyword in C#?
- 5.7 Q: How is the ‘override’ keyword used in C#?
- 5.8 Related
Types of polymorphism in C#
There are two types of polymorphism in C#:
- Compile Time Polymorphism / Static Polymorphism (method overloading)
- Run-Time Polymorphism / Dynamic Polymorphism (method overriding)
01. Compile Time Polymorphism
Compile Time Polymorphism in C# refers to defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameters. It allows us to perform different tasks with the same method name by passing different parameters.
- Compile time polymorphism is also known as method overloading, early binding, or static binding.
- In compile-time polymorphism, the compiler identifies which method is need to be called at compile-time rather than runtime.
Rules for Method Overloading:
Method overloading in C# is a feature of object-oriented programming that allows a class to have multiple methods with the same name, but with different signatures (parameters). There are several rules that must be followed when overloading a method:
- Method Signature: The first rule to overload a method in C# is to change the method signature. Either the number of arguments, type of arguments, or order of arguments must be different types.
- Method Return Type: The return type of the method is not part of the method overloading, so simply changing the return type will not overload a method in C#.
- Access modifier: The access modifier of the overloaded method can be the same or different.
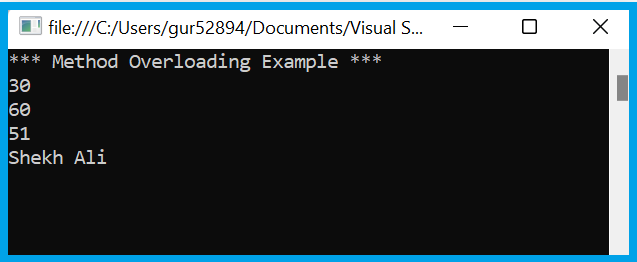
The following example shows method overloading by defining multiple Add methods with different types and numbers of parameters
using System;
namespace MethodOverloadingExample
{
class Program
{
public void Add(int num1, int num2)
{
Console.WriteLine(num1 + num2);
}
public void Add(int num1, int num2, int num3)
{
Console.WriteLine(num1 + num2 + num3);
}
public void Add(float x, float y)
{
Console.WriteLine(x + y);
}
public void Add(string str1, string str2)
{
Console.WriteLine(str1 + " " + str2);
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program program = new Program();
Console.WriteLine($"*** Method Overloading Example ***");
program.Add(10, 20);
program.Add(10, 20, 30);
program.Add(20.5f, 30.5f);
program.Add("Shekh", "Ali");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output:
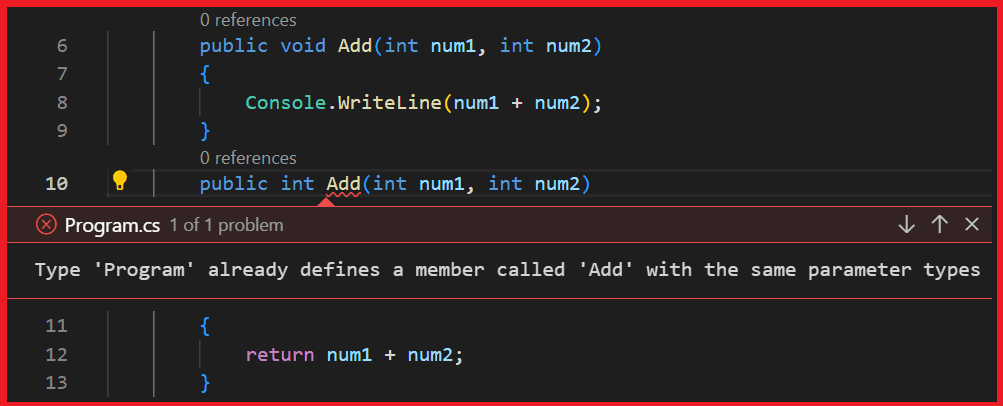
Example: Invalid Method overloading using different return type
As we already know the return type of methods is not considered as method overloading. The following example will give a compile-time error.
public void Add(int num1, int num2)
{
Console.WriteLine(num1 + num2);
}
public int Add(int num1, int num2)
{
return num1 + num2;
}
Once we run the application we will get the compilation error:
02. Dynamic / Runtime Polymorphism
Method overriding, also known as runtime polymorphism. It is a feature in C# that allows a subclass to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already defined in its superclass or base class. This enables a derived class to provide a specialized version of a method already defined in its base class.
Key points about method overriding and runtime polymorphism in C#:
- Inheritance Requirement: Method overriding is possible only when there is an inheritance relationship between the base class (parent class) and the derived class (child class).
- Same Signature: The method in the derived class must have the same signature (name, return type, and parameters) as the method in the base class that it intends to override.
- Override Keyword: The override keyword is used in the derived class to indicate that a method is intended to override a method in the base class.
Runtime Polymorphism is also known as Dynamic binding or Late binding where the method that needs to be called is determined at the run-time rather than at compile-time.
We can achieve Runtime polymorphism using override & virtual keywords, and inheritance principles.
Runtime polymorphism Example1:
using System;
class Animal
{
public virtual void MakeSound()
{
Console.WriteLine("Animal makes a generic sound");
}
}
class Cat : Animal
{
public override void MakeSound()
{
Console.WriteLine("Cat purrs");
}
}
class Dog : Animal
{
public override void MakeSound()
{
Console.WriteLine("Dog barks");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Animal pet1 = new Cat();
Animal pet2 = new Dog();
Console.WriteLine("Pet 1 sound:");
pet1.MakeSound(); // Calls the overridden method in Cat class
Console.WriteLine("\nPet 2 sound:");
pet2.MakeSound(); // Calls the overridden method in Dog class
}
}
Output:
Pet 1 sound:
Cat purrs
Pet 2 sound:
Dog barksCode Explanation:
In this example, we have an Animal base class with a virtual method MakeSound.
The Cat and Dog classes are derived from Animal and override the MakeSound method with their specific implementations.
The Main method shows how you can use polymorphism to call the overridden methods based on the actual runtime type of the objects.
Method Overriding Example2:
In the following code example, we have defined an Area() method with a virtual keyword in the base class named Shape, which allows the derived classes named Circle and Square to override this method using the override keyword.
using System;
namespace MethodOverridingExample
{
abstract class Shape
{
// Virtual method
public virtual double Area()
{
return 0;
}
}
class Circle : Shape
{
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius)
{
this.radius = radius;
}
// Override method
public override double Area()
{
return (3.14 * radius * radius);
}
}
class Square : Shape
{
private double side;
public Square(double square)
{
side = square;
}
// Override method
public override double Area()
{
return (side * side);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Circle circle = new Circle(5);
Square square = new Square(10.5);
Console.WriteLine($" Area of Circle = {circle.Area()}");
Console.WriteLine($" Area of Square = {square.Area()}");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Output:
Area of Circle = 78.5
Area of Square = 110.25
Rules for method overriding
It’s important to follow the following rules when overriding a method because they ensure that the child class maintains the expected behavior of the method and does not violate the contract established by the base or superclass.
- A child class method must have the same name, return type, and number and type of parameters as the method defined in the base class. This is required because the child class is overriding and providing a new implementation of an existing method and needs to maintain the same interface as the original method.
- The method in the child class or subclass must have the same or a more restrictive access modifier than the method in the base or superclass. For example, if the method in the base class is public, the method in the child class can also be public, but it cannot be less accessible, such as protected or private.
- The method in the child class should not be sealed. If the method in the base class is sealed, it cannot be overridden in the child class. A sealed method is a method that cannot be overridden or modified by a child/subclass.
FAQs
Q: How many different types of polymorphism are there in C#?
Polymorphism in C# is classified into two types: compile-time polymorphism and runtime polymorphism.
C# supports compile-time (static) polymorphism through method overloading and runtime (dynamic) polymorphism through method overriding.
Q: What is dynamic or runtime polymorphism in C#?
Runtime polymorphism is achieved through method overriding in a derived class. This process involves the use of the reference variable of a base class to call for an overridden method of the child class.
Q: What is the main difference between overriding and overloading?
Overriding occurs when the method signature is the same in the base class and the child class. Overloading, on the other hand, occurs when two or more methods in the same class have the same name but different parameters.
Q: What is the purpose of polymorphism in C#?
Polymorphism in C# allows us to reuse code by writing a single function that can be used for multiple purposes.
Q: Can you give a good example of polymorphism?
A good example of polymorphism is a person who can have multiple characteristics at the same time. A man is a father, a husband, and an employee all at the same time. So, the same person can behave differently in different situations.
Q: What is the ‘virtual’ keyword in C#?
The ‘virtual’ keyword is used to declare a method in a base class that can be overridden in derived classes. It enables runtime polymorphism.
Q: How is the ‘override’ keyword used in C#?
The ‘override’ keyword is used in a derived class to provide a specific implementation for a method that is already defined in its base class.
References: MSDN-Polymorphism
Related articles:
- C# Abstract class Vs Interface
- C# Array Vs List
- ref and out keyword
- C# Dictionary with Examples
- Difference between Boxing and Unboxing in C#
- C# List Class With Examples
- C# Stack Class With Push And Pop Examples
- C# Struct vs Class
- C# Hashtable vs Dictionary
- C# Nullable types: How do you work with nullable types in C#?
- Top 5 Differences between Call by Value and Call by Reference
- C# Unsafe Code: Why do we need unsafe code in C#?
- Params Keyword in C# With Examples
- Difference Between Array And ArrayList In C#: Choosing the Right Collection - May 28, 2024
- C# Program to Capitalize the First Character of Each Word in a String - February 21, 2024
- C# Program to Find the Longest Word in a String - February 19, 2024