C# is a versatile programming language that offers developers a wide range of features. One of the most important features is string formatting. C# String formatting allows developers to format their strings according to specific requirements, which makes it easier to read and display data in different formats.
In this article, we will discuss how to format string in C# in different ways using examples.
Table of Contents
- 1 C# String Format() Method
- 2 C# Date Time Formats
- 3 Example 1: C# Format() With Date Time
- 4 Example 2: Format dates using String.Format()
- 5 C# Number Formats
- 6 Example : C# Format() With Numbers
- 7 Insert a single object in a C# string.
- 8 Insert multiple objects in a C# string.
- 9 Convert a number to hexadecimal in C# using String.Format() Method:
- 10 Formatting String Using String Interpolation:
- 11 FAQs
- 11.1 Q: What is the difference between String.Format and StringBuilder?
- 11.2 Q: Can you use named format items in C#?
- 11.3 Q: Can you use format specifiers with custom types?
- 11.4 Q: What is string formatting in C#?
- 11.5 Q: What are format specifiers in C#?
- 11.6 Q: What are some common format specifiers for formatting numbers in C#?
- 11.7 Q: How to format string in C#?
- 12 Conclusion:
C# String Format() Method
The String.Format method is used to format strings in C#. It is a powerful method that can format any kind of data, including dates, times, numbers, and more.
The Format method takes objects as input and converts their values to strings according to specified formats. These formatted strings are then inserted into a separate string.
a. Syntax:
The syntax for the Format() method is as follows:
string output = String.Format(format, arg0, arg1, ...);- format – a format string
- arg – the object to format
b. Example:
using System;
class StringFormatExample
{
static void Main()
{
string name = "Shekh";
int age = 29;
string message = String.Format("My name is {0} and I am {1} years old.", name, age);
Console.WriteLine(message);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}Output:
My name is Shekh and I am 29 years old.In the example above, we used the String.Format method to format a string with two arguments. We replaced placeholders {0} and {1} with the variable’s name and age values, respectively.
C# Date Time Formats
C# offers a wide range of date and time formatting options that we can use as per our project requirements. Here are some of the most commonly used ones:
- “d”: Short date format (e.g. 3/3/2023).
- “D”: Long date format (e.g. Friday, March 3, 2023).
- “t”: Short time format (e.g. 5:26 PM).
- “T”: Long time format (e.g. 5:26:36 PM).
- “f”: Full date/time with short time format (e.g. Friday, March 3, 2023 5:26 PM).
- “F”: Full date/time with long time format (e.g. Friday, March 3, 2023 5:26:36 PM).
- “g”: General date/time format (e.g. 3/3/2023 5:26 PM).
- “G”: General date/time with long time format (e.g. 03/03/2023 17:26:36).
Example 1: C# Format() With Date Time
The following output shows the formatted date and time values using each of the format specifiers.
using System;
class StringFormatExample
{
static void Main()
{
DateTime now = DateTime.Now;
string shortDate = string.Format("Short date format: {0:d}", now);
string longDate = string.Format("Long date format: {0:D}", now);
string shortTime = string.Format("Short time format: {0:t}", now);
string longTime = string.Format("Long time format: {0:T}", now);
string fullDateTimeWithShortFormat = string.Format("Full DateTime With Short Format: {0:f}", now);
string fullDateTimeWithLongFormat = string.Format("Full DateTime With Long Format: {0:F}", now);
string GeneraldateTimeFormat = string.Format("General date/time format: {0:g}", now);
string GeneraldateTimeLongFormat = string.Format("General date/time Long format: {0:G}", now);
string customFormat = string.Format("Custom date and time format: {0:dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss}", now);
Console.WriteLine(shortDate);
Console.WriteLine(longDate);
Console.WriteLine(shortTime);
Console.WriteLine(longTime);
Console.WriteLine(fullDateTimeWithShortFormat);
Console.WriteLine(fullDateTimeWithLongFormat);
Console.WriteLine(GeneraldateTimeFormat);
Console.WriteLine(GeneraldateTimeLongFormat);
Console.WriteLine(customFormat);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}Output:
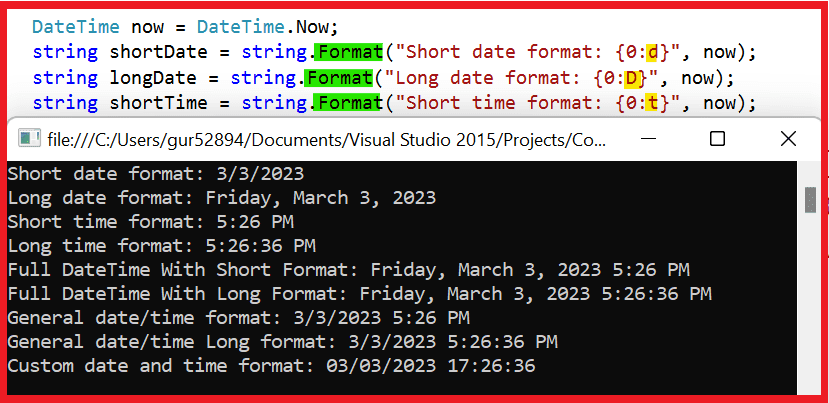
In the above example, we use the DateTime.Now property to get the current date and time. We then use the string.Format method to format the date and time values using various standard and custom date and time format strings.
The d format specifier is used for short date format, D for long date format, t for short time format, and T for long time format. The custom format string dd/MM/yyyy HH:mm:ss specifies the day, month, year, hours, minutes, and seconds components of the date and time value.
Example 2: Format dates using String.Format()
Here is an example of formatting date using String.Format() in C#:
DateTime myDate = new DateTime(2023, 5, 2);
string formattedDate = String.Format("Formatted Date is {0:dddd, MMMM d, yyyy}", myDate);
Console.WriteLine(formattedDate);
Output:
Formatted Date is Tuesday, May 2, 2023Code Explanation:
In this example, we create a DateTime object called myDate and set it to a specific date using the constructor that takes year, month, and day arguments.
We then use String.Format() to format this date as a string. The String we provide as the first argument contains a format specifier ({0:dddd, MMMM d, yyyy}) that tells String.Format() how to format the date.
The format specifier consists of the following elements:
- {0}: This specifies that the first argument to String.Format() (in this case, the now variable) should be used as the input value for formatting.
- dddd: This is a custom format specifier representing the full name of the day of the week (e.g., “Tuesday”).
- ,: This is a literal character that will be included in the output.
- MMMM: This is a custom format specifier that represents the full name of the month (e.g., “May”).
- d: This is a custom format specifier that represents the day of the month as a number (e.g., “2”).
- yyyy: This custom format specifier represents the year as a four-digit number (e.g., “2023”).
To know more about date time formatting, please refer to this article: DateTime Format in C#
C# Number Formats
Numeric values can be formatted using format specifiers that define the format of the number. Some commonly used number format specifiers are:
| Format Specifier | Description | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| c | Currency format | {0:c} | $1,234.56 |
| d | Decimal format | {0:d} | 1234 |
| e | Scientific notation | {0:e} | 1.234E+003 |
| f | Fixed-point format | {0:f} | 1234.56 |
| g | General format | {0:g} | 1234.56 or 1.234E+003 |
| n | Number format with thousands separator | {0:n} | 1,234.56 |
| p | Percentage format | {0:p} | 50.00 % |
| x | Hexadecimal format | {0:x} | 4D2 |
| X | Hexadecimal format with capital letters | {0:X} | 4D2 |
Example : C# Format() With Numbers
using System;
class StringFormatExample
{
static void Main()
{
int number = 123456789;
// Standard Numeric Format Specifiers
string currency = string.Format("Currency format: {0:C}", number);
string decimalPlaces = string.Format("Decimal places format: {0:F2}", number);
string percentage = string.Format("Percentage format: {0:P}", number);
string scientific = string.Format("Scientific format: {0:E}", number);
// Custom Numeric Format Specifiers
string thousandsSeparator = string.Format("Thousands separator format: {0:#,0}", number);
string customDecimalPlaces = string.Format("Custom decimal places format: {0:0.00}", number);
string customPercentage = string.Format("Custom percentage format: {0:0.00%}", number);
Console.WriteLine(currency);
Console.WriteLine(decimalPlaces);
Console.WriteLine(percentage);
Console.WriteLine(scientific);
Console.WriteLine(thousandsSeparator);
Console.WriteLine(customDecimalPlaces);
Console.WriteLine(customPercentage);
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Number: {0:N}", 125)); // Number: 125.00
Console.ReadKey();
}
}Output:
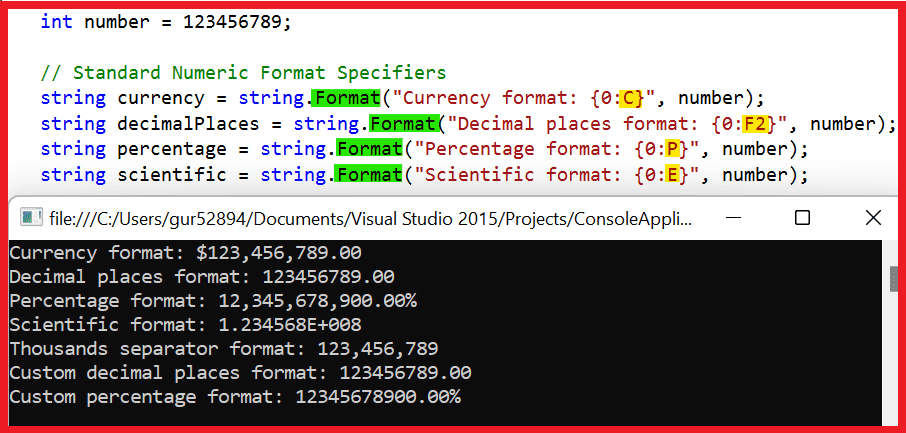
Insert a single object in a C# string.
To insert a single object in a C# string, you can use the {0} format specifier, where 0 is the index of the argument to insert.
using System;
class StringFormatExample
{
static void Main()
{
string name = "Shekh Ali";
string message = string.Format("Hello, {0}!", name);
Console.WriteLine(message);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
// Output: Hello, Shekh Ali!Insert multiple objects in a C# string.
To insert multiple objects in a C# string, you can use multiple format specifiers and arguments separated by commas.
using System;
class StringFormatExample
{
static void Main()
{
string firstName = "John";
string lastName = "Cena";
int age = 30;
string message = string.Format("My name is {0} {1} and I'm {2} years old.", firstName, lastName, age);
Console.WriteLine(message);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
// Output: My name is John Cena and I'm 30 years old.Convert a number to hexadecimal in C# using String.Format() Method:
Here is an example of using the String.Format() method to convert a number to hexadecimal in C#:
using System;
class NumberToHexaDecimal
{
static void Main()
{
int num = 42;
string hex = String.Format("{0:X}", num);
Console.WriteLine(hex); // Output: 2A
Console.ReadKey();
}
}In this example, the integer num is set to 42. Then, the String.Format() method converts the value of num to a hexadecimal string using the format specifier {0:X}. The X format specifier tells the method to use hexadecimal format.
Formatting String Using String Interpolation:
Starting with C# 6.0, you can use string interpolation to format strings instead of the String.Format() method. String interpolation allows you to include variables directly in the String using the $ symbol and use braces to enclose expressions. For example:
using System;
class StringInterpolation
{
static void Main()
{
string name = "Robert";
int age = 30;
string interpolated = $"My name is {name} and I am {age} years old.";
Console.WriteLine(interpolated);
// Output: My name is Robert and I am 30 years old.
Console.ReadKey();
}
}FAQs
Q: What is the difference between String.Format and StringBuilder?
String.Format is a method that returns a formatted string, while StringBuilder is a class that provides a way to efficiently build strings by appending characters to a buffer.
Q: Can you use named format items in C#?
Yes, you can use named format items in C# by enclosing the name in braces, like this: {firstName}. You must also provide a named argument with the same name as the format item.
Q: Can you use format specifiers with custom types?
Yes, you can use format specifiers with custom types by implementing the IFormattable interface in your class.
Q: What is string formatting in C#?
String formatting in C# is the process of converting a set of input values into a formatted string that can be displayed to the user or used in other parts of the program.
It is typically done using the String.Format() method or similar methods that take input values and format them according to specified format strings.
Q: What are format specifiers in C#?
Format specifiers in C# are codes used within format strings to specify how input values should be formatted. These codes can specify things like the number of decimal places to display, whether to display a value as a currency, and so on.
The specific format specifiers that are available depend on the type of input value being formatted.
Q: What are some common format specifiers for formatting numbers in C#?
Some common format specifiers for formatting numbers in C# include C for currency format, F for the fixed-point format, N for number format with thousands separators, E for scientific notation format, and P for percentage format. Many other format specifiers are also available, depending on the specific formatting needs of the program.
Q: How to format string in C#?
The String.Format() method in C# can be used to format strings with various parameters, such as dates and numbers. The method converts the value of objects to strings based on the formats specified and inserts them into another string.
Example:
string phoneNumber = “1234567890”;
string formattedNumber = String.Format(“({0}) {1}-{2}”, phoneNumber.Substring(0, 3), phoneNumber.Substring(3, 3), phoneNumber.Substring(6));
Console.WriteLine(“Formatted phone number: {0}”, formattedNumber);
//Output: Formatted phone number: (123) 456-7890
References: Msdn-String.Format() Method
Conclusion:
This article taught us how to format strings, numeric values, and DateTime values. We have also seen examples of inserting single and multiple objects in a C# string using format specifiers.
Understanding these concepts allows you to write more efficient and effective code in C#. Remember to experiment with different format specifiers to achieve the desired output, and always test your code thoroughly.
Articles you might also like:
- DateTime Format in C#
- String Vs StringBuilder in C#
- Different Ways to Calculate Factorial in C# (with Full Code Examples)
- 10 Differences between interface and abstract class In C#
- Fibonacci sequence: Fibonacci series in C# (with examples)
- C# Operators with [Examples]
- C# Goto Statement
- C# switch Statement (With Examples)
- C# System.IO Classes: An Overview of the System.IO Namespace
- Design Patterns
- SOLID Design Principles in C#: A Complete Example
- Singleton Design Pattern in C#: A Beginner’s Guide with Examples
- Abstract Factory Design Pattern in C#
- Local vs Global Variables
- C# stack vs heap
- IEnumerable Interface in C# with examples
- Constructors in C# with Examples
- C# Dictionary
- Is vs As operator in C#
Please share this post and let us know what you think in the comments.
- C# 12 New Features in 2025: What’s New with .NET 8 - April 11, 2025
- Difference Between WCF and Web API with Examples: A Comprehensive Guide - March 27, 2025
- PUT vs PATCH vs POST in REST API: Key Differences Explained With Examples - March 23, 2025